Create Cloud RADIUS Network Policies
How to Create Cloud RADIUS Network Policies - Video Tutorial
Prerequisites
- Registering the application in your tenant
- Creating Cloud Radius Instance
- Being a Subscription Owner or Network Administrator
Introduction - Managing your Cloud RADIUS Network Policies in EZRADIUS
Network policies are used to define the conditions under which a user or device can connect to your network. In this page we will go through how to create network policies in EZRADIUS.
- Go to your EZRADIUS portal.
- Click on “Policies”.
What are the RADIUS Server Details?
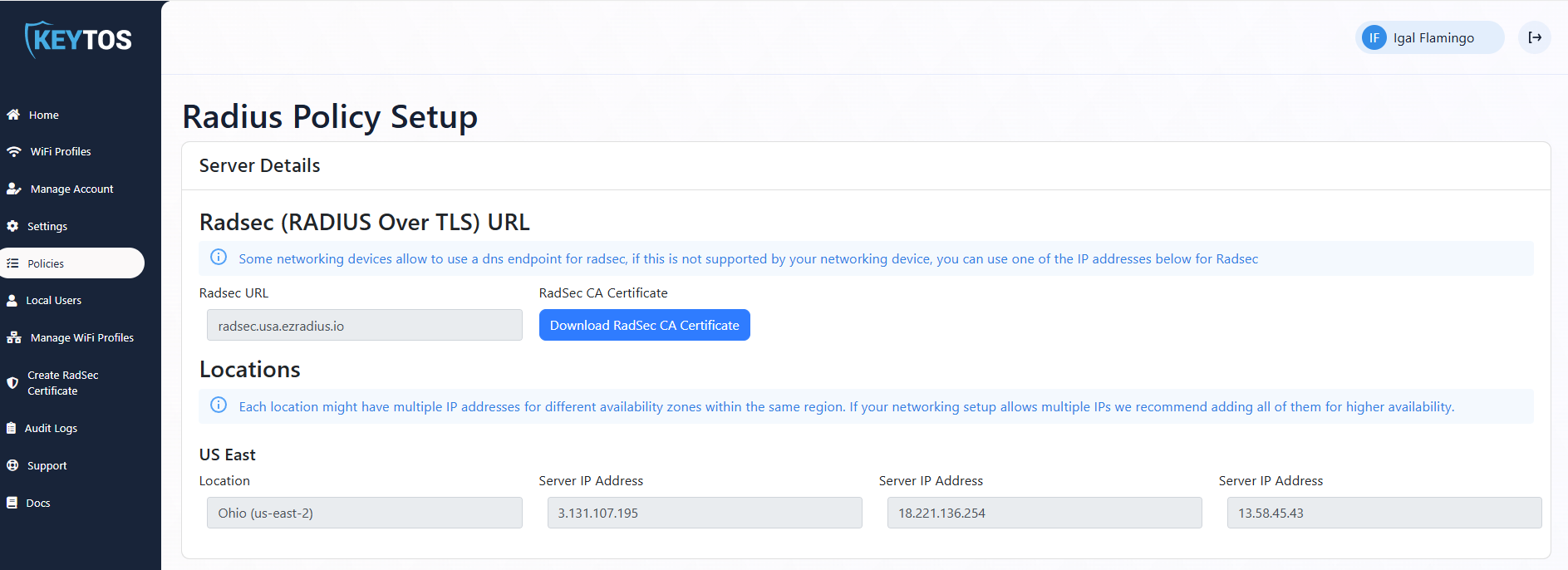
At the top of the page, you will see the server details. These are the details that you will need to connect to the cloud RADIUS service. EZRADIUS offers two different ways to connect “Regular” RADIUS (which is over port 1812 for Authentication and port 1813 for Accounting), and radsec (RADIUS over TLS) (which uses port 2083). Depending on which one you are using you will need different the different server details that are in this section. Note: while the Radsec Section only has a url, you can use an IP address for the Radsec server if your firewall does not support SNI.
Create a new RADIUS Network Policy
Before we dive into creating a new RADIUS network policy, let’s understand the different components of a network policy. Each policy has the following components:
- Name: A unique name for the policy.
- Radsec Accepted Certificate Authorities or Certificates: The certificate authorities and/or certificates that are accepted for the Radsec authentication. These certificates authorities and/or certificates will be used to authenticate your networking infrastructure to our cloud RADIUS with Radsec.
- Classic RADIUS: The IP addresses that are allowed to connect to your Cloud RADIUS server (these are the Public IP addresses of your access points).
- Accepted Certificate Authorities: The certificate authorities that are accepted by the RADIUS server. These CAs are used to validate the certificates of the devices connecting to the network.
- Server Certificate: EAP-TLS requires the server uses a certificate that the devices trust for identification of the server. This is the server certificate.
- Access Policies: The conditions under which a user or device can connect to your network. This includes the authentication methods, the network policies, and the user groups that are allowed to connect as well as VLAN rule assignment. Each policy can have multiple access policies and they are checked in the order they are sorted.
Now that we understand the components of a network policy, let’s create a new policy.
Set up a new RADIUS Network Policy
First we must set the policy Name. Enter the Policy name.
Enable Radsec and/or Classic RADIUS
Next we have to enable which authentication methods you are going to use, you can use Radsec, Classic RADIUS, or both.
How to Set Up Radsec for Cloud RADIUS
If you enabled Radsec, you have to add a certificate authority or certificate that is accepted by the RADIUS server. This is dependant on your networking device (for example, if you are using a Cisco device, you will need to add the Root CA of the certificate that signed the certificate of the device, if you are using a Ubiquiti device, it allows you to upload your own certificate from your CA).
Add Certificate Authorities to Radsec Using EZCA (Option 1)
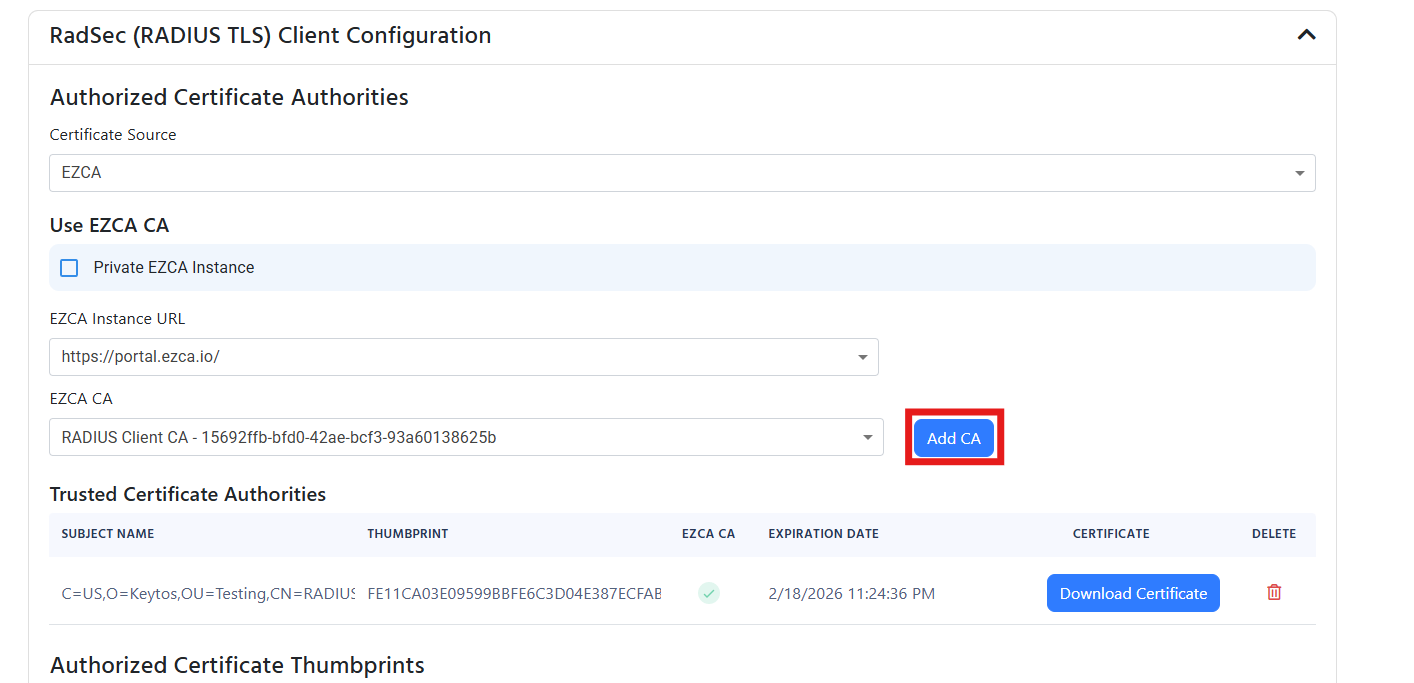
If your Radsec certificate is issued by your EZCA Certificate Authority, then you can easily add the CA to the cloud RADIUS server by:
- Selecting your EZCA instance from the dropdown.
- Selecting the CA you want to add to the RADIUS server.
- Click “Add CA” to add the CA to the RADIUS server.
Add Certificate Authorities to Radsec Using 3rd Party CA (Option 2)
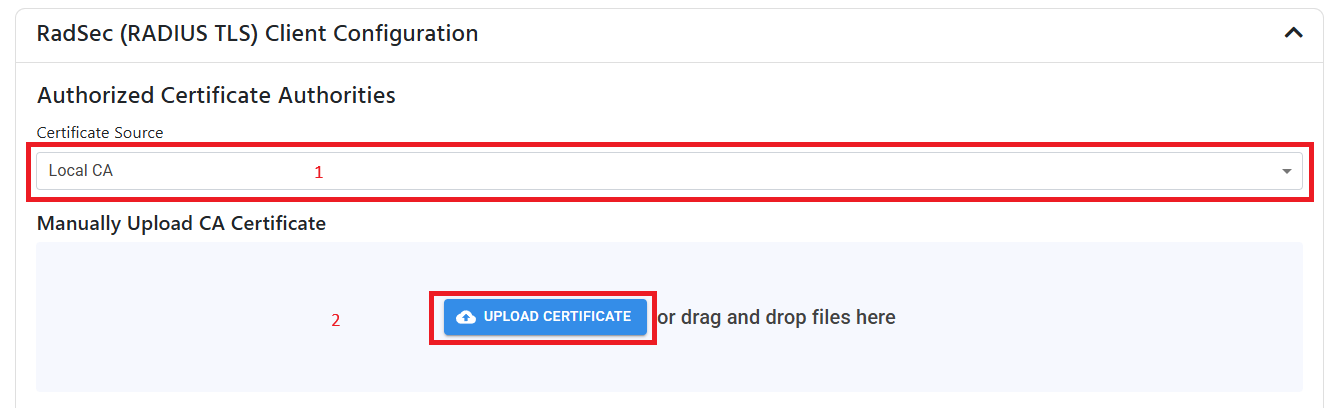
If your device uses a certificate from a 3rd party CA, you can add the CA to the cloud RADIUS server by:
- Switching the Certificate Source to “Local CA”.
- Uploading the CA certificate in PEM format.
Add Self-Signed Certificate to Radsec (Option 3)
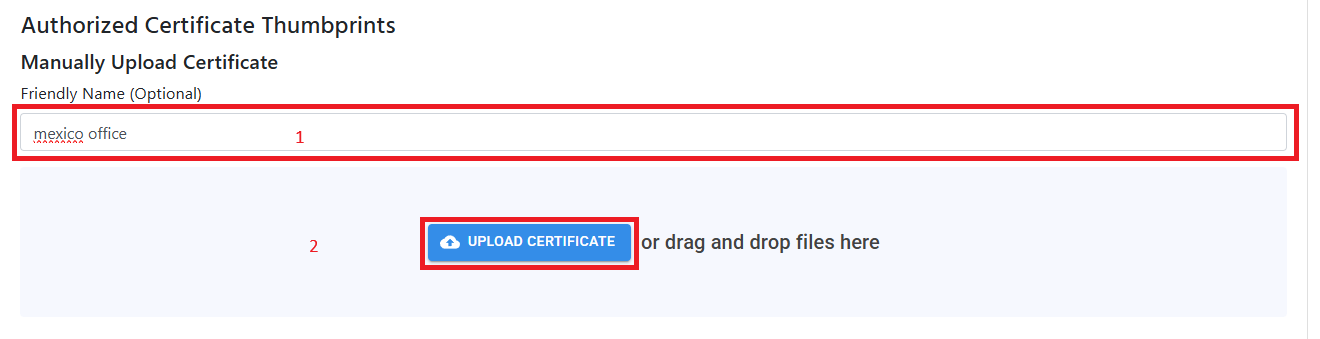
If your networking device only does self-sign certificates for Radsec, you can upload the single certificate to your cloud RADIUS policy by:
- Entering a Certificate Friendly Name (This is just for your records, useful if have multiple locations).
- Uploading the certificate in PEM format.
How to Set Up RADIUS Authentication for Cloud RADIUS
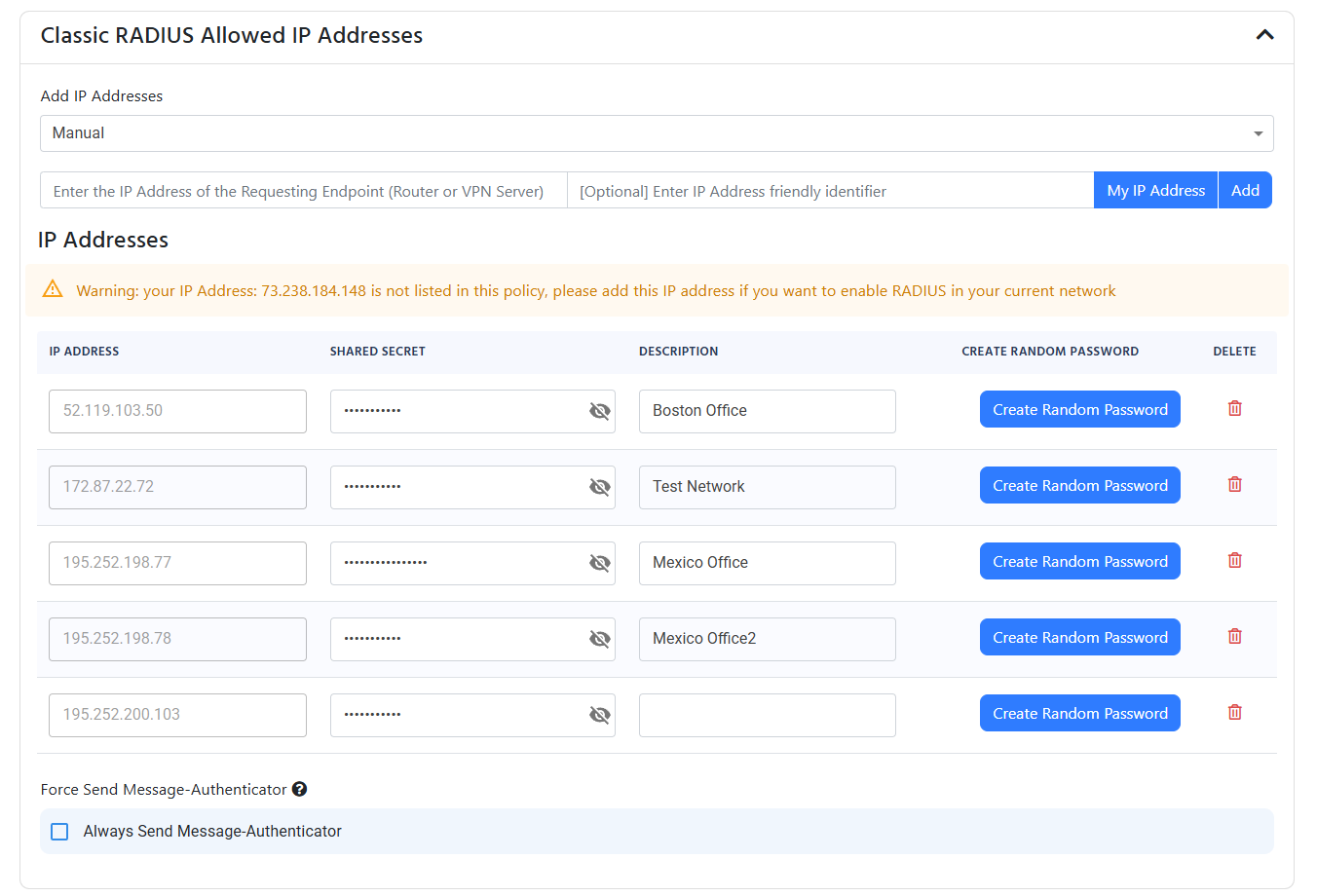
The other option is to do regular RADIUS authentication over UDP (don’t worry, the credentials are still encrypted by EAP-TLS or EAP-TTLS). If you enabled Classic RADIUS, you have to add the public IP addresses of your locations that are allowed to connect to the RADIUS server.
If using Fortinet devices, After Fortigate 7.2.10 you will need to enable the “Always Send Message Authenticator” option in the RADIUS server settings. 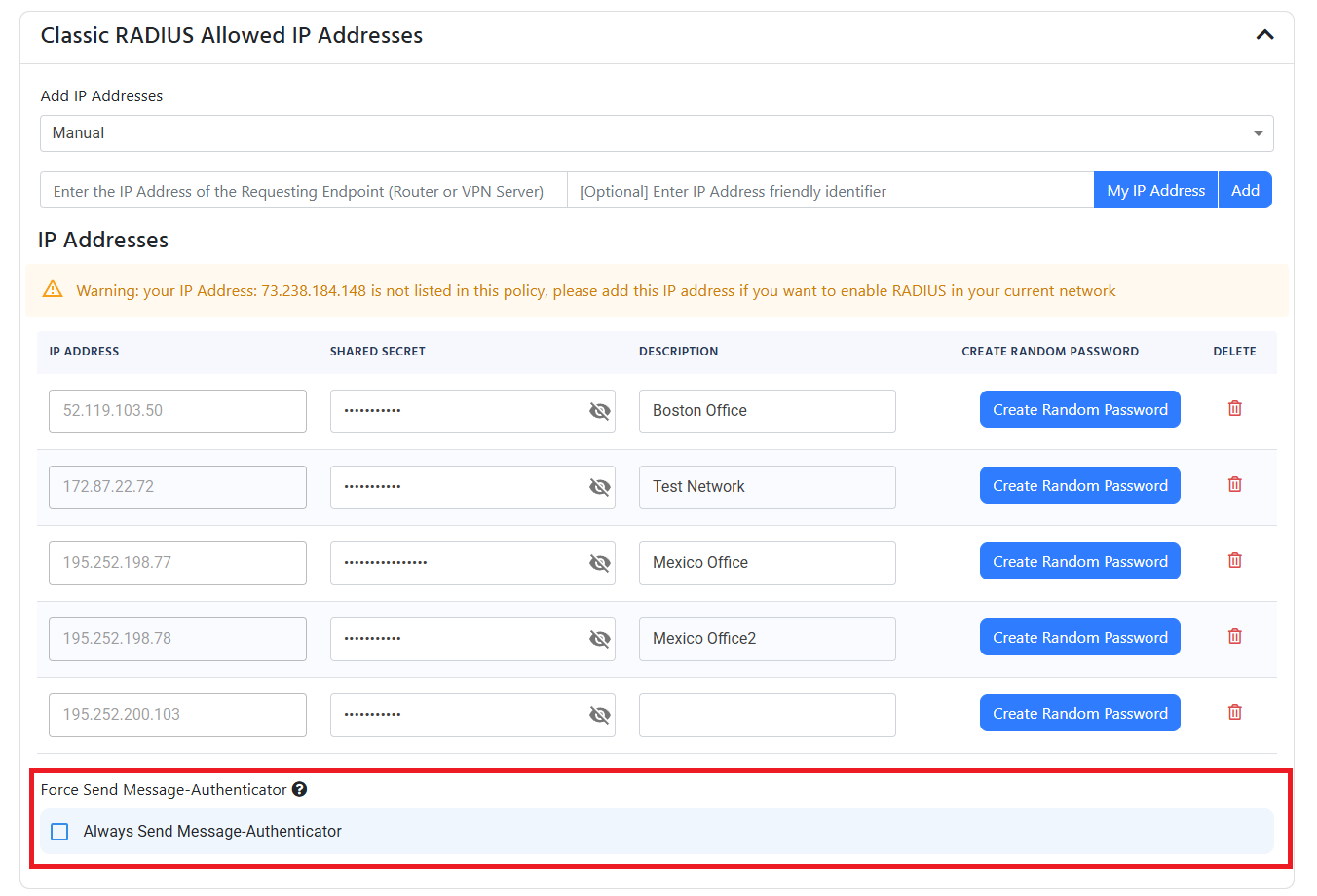
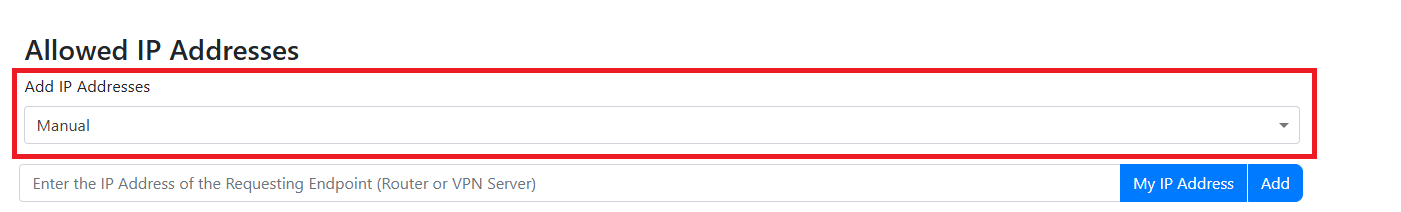
Add IP Addresses to RADIUS Network Policy (Manually)
This IP address is the external IP address for your network. It should not start with 192.168, 10.0, 172.16, or any other private IP address range.
- Enter the IP addresses of your access points by entering the IP Address and entering add. When you click “Add” the IP address will be added to the list of allowed IP addresses and a random shared secret will be created, if you want to change the secret, you can change it in the text field for the shared secret. You will need to configure your network devices with the shared secret.
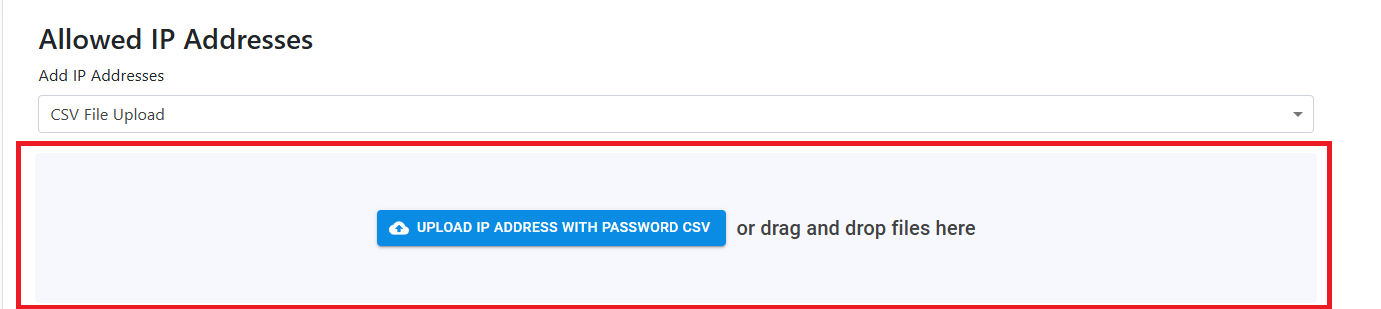
Add IP Addresses to RADIUS Network Policy (Using CSV)
If you have multiple IP Addresses you can add them using a CSV file (if you have an CIDR range and want to convert it to IP range, use this site). The CSV file must have the following format:
12.12.12.12,friendlyname,SharedSecret1
12.12.12.13,SecondName,SharedSecret2
- Once you have your CSV file, select “CSV File Upload” from the dropdown.
- And then upload or drag the CSV file to the upload area.
Add Certificate Authorities to RADIUS for Certificate Authentication
If you are using Certificate Authentication (highly recommended if using an MDM due to the extra security and seamless user experience), we must add the Certificate Authorities we trust to the RADIUS Service, if you are using EZCA our cloud based Certificate Authority, It is a few clicks away, if you are using a different CA, you can upload the CA certificate in PEM format, below you can see the steps to add the CA using each option.
Add Certificate Authorities to RADIUS Using EZCA (Option 1)
- If you are using EZCA, Ensure that EZCA is set as the certificate source, then from the dropdown select your EZCA instance (If you are using an EZCA private instance select the private instance checkbox and enter your EZCA URL).
- You should now have a dropdown with the CAs you have in your EZCA instance, select the CA you want to add to the RADIUS server.
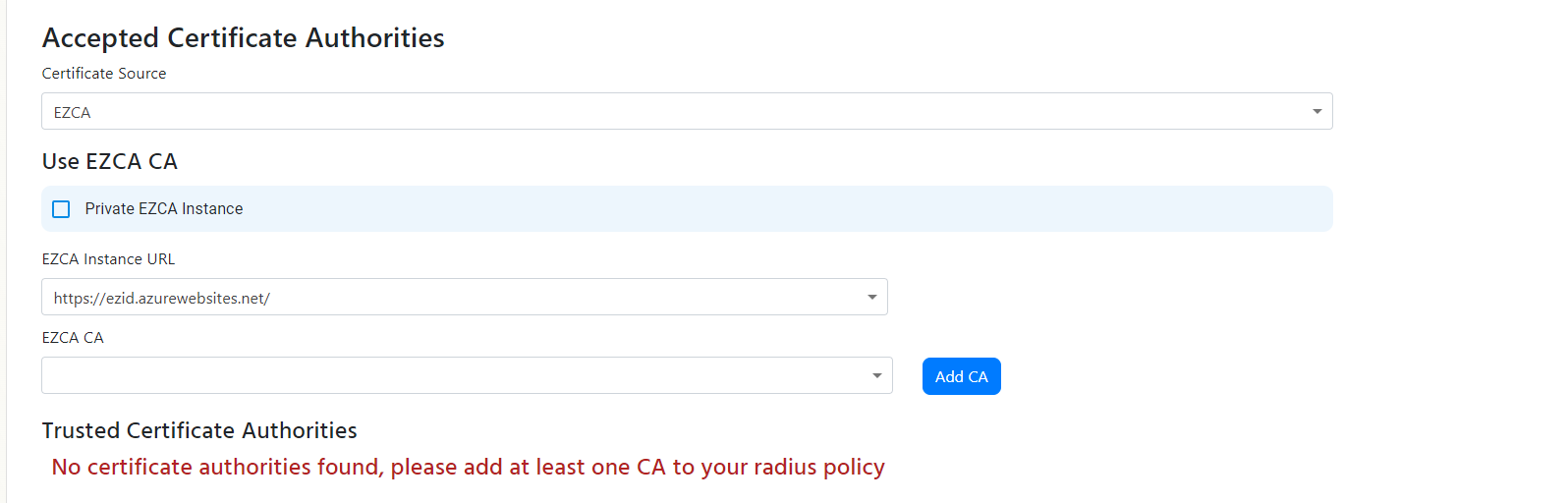
- Select the CAs you want to add and click “Add” (If you have a 2 tier hierarchy please add both your Root CA and your Issuing CA). EZCA and EZRADIUS will take care of the rest.
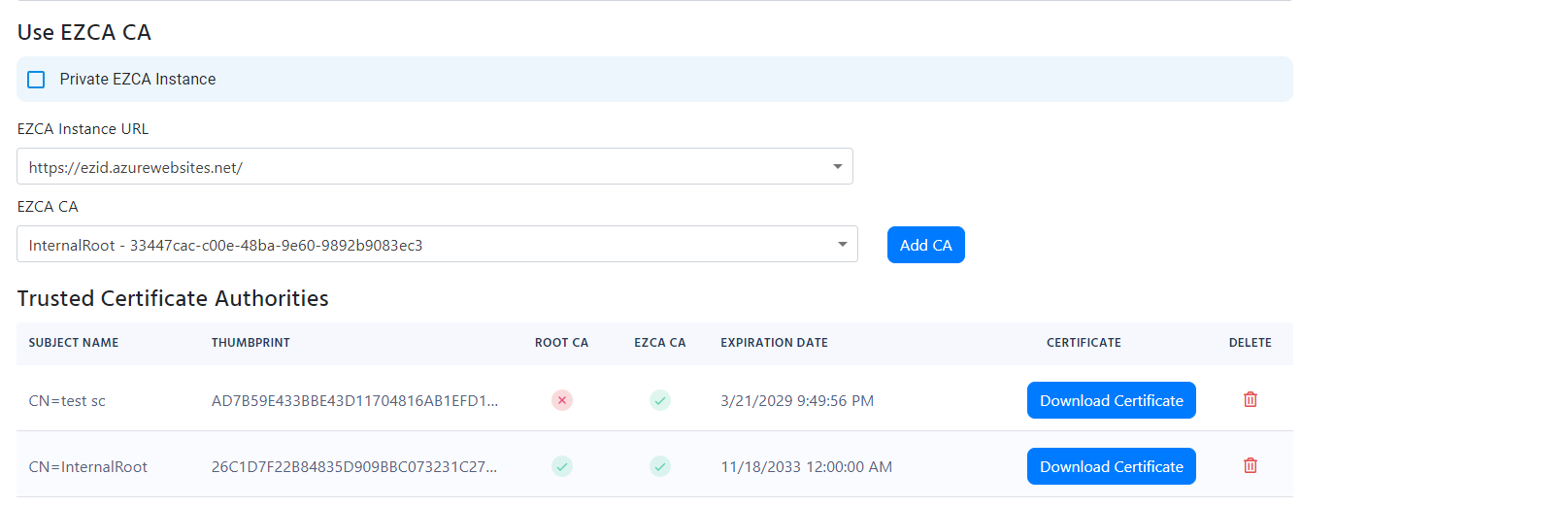
Add Certificate Authorities to RADIUS Using 3rd Party CA (Option 2)
- If you are using a 3rd party CA, ensure that “Local CA” is set as the certificate source.
- If you are uploading a Root CA, check the “Root CA” checkbox, if you are uploading an Issuing CA, leave the checkbox unchecked.
- Click on “Upload Certificate” and select the CA certificate in PEM format.
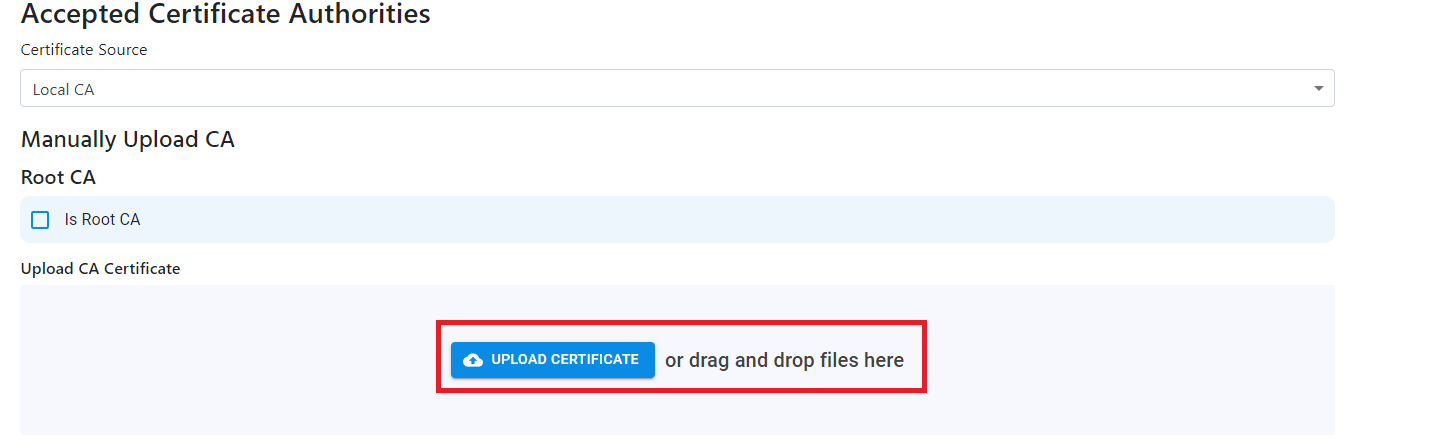
- Repeat the process for all the CAs you want to add (If you have a 2 tier hierarchy please add both your Root CA and your Issuing CA).
Add Server Certificate to RADIUS
The Next step is to add the server certificate to the RADIUS server. This certificate is used to identify the RADIUS server to the devices connecting to the network. For this, you can use a certificate from EZCA or a 3rd party CA. Below you can see the steps to add the server certificate using each option.
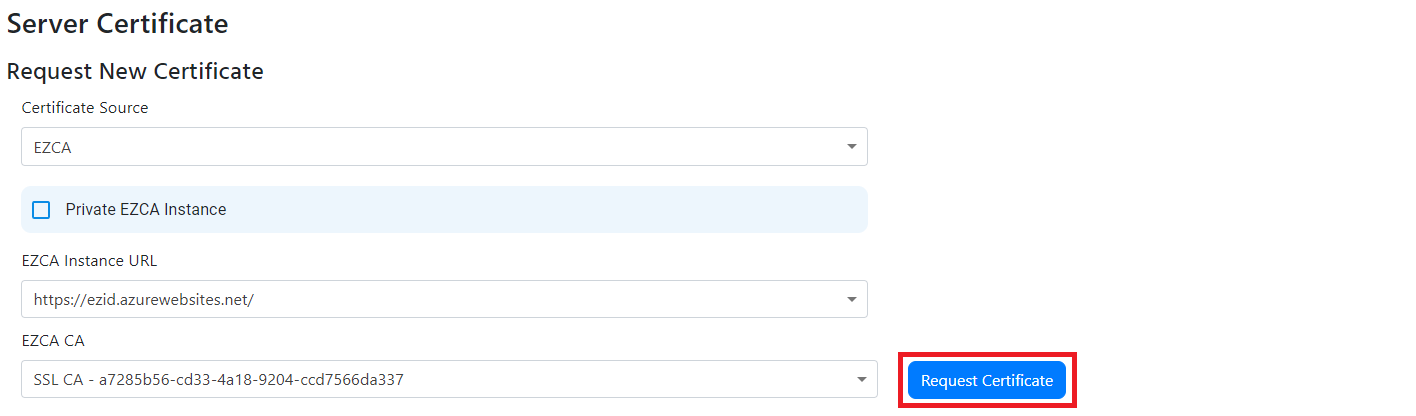
Add Server Certificate to RADIUS Using EZCA (Option 1)
- If you are using EZCA, Ensure that EZCA is set as the certificate source, then from the dropdown select your EZCA instance (If you are using an EZCA private instance select the private instance checkbox and enter your EZCA URL).
- You should now have a dropdown with the certificates authorities you have in your EZCA instance, select the CA you want to use.
EZRADIUS will connect to EZCA and create the certificate. This certificate will be automatically renewed by EZRADIUS.
- Click “Add” to add the certificate to the RADIUS server.
- You should now see the certificate in the list of certificates.
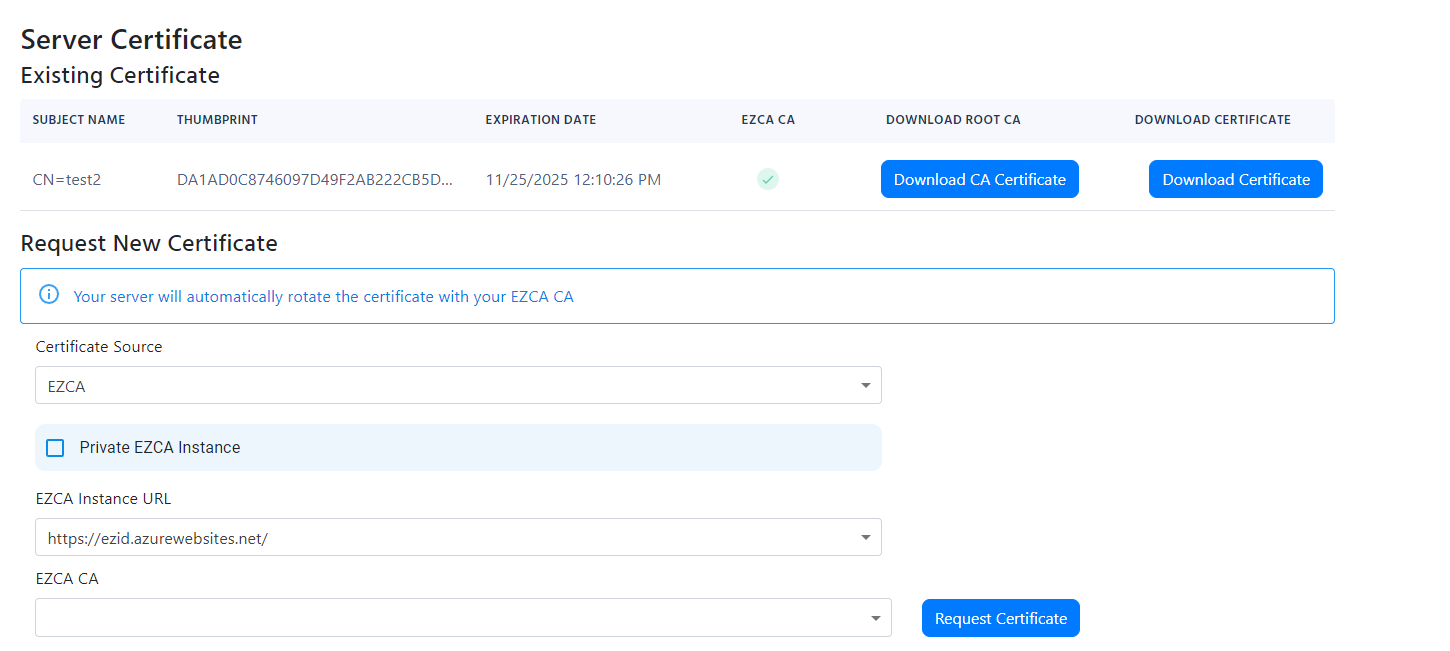
Create a Free Certificate with Integrated Certificate Authority (Option 2)
- If you do not have a your own CA, you can use the integrated CA to create a free certificate.
- Select “Auto-Generated Certificate” from the Certificate Source dropdown.
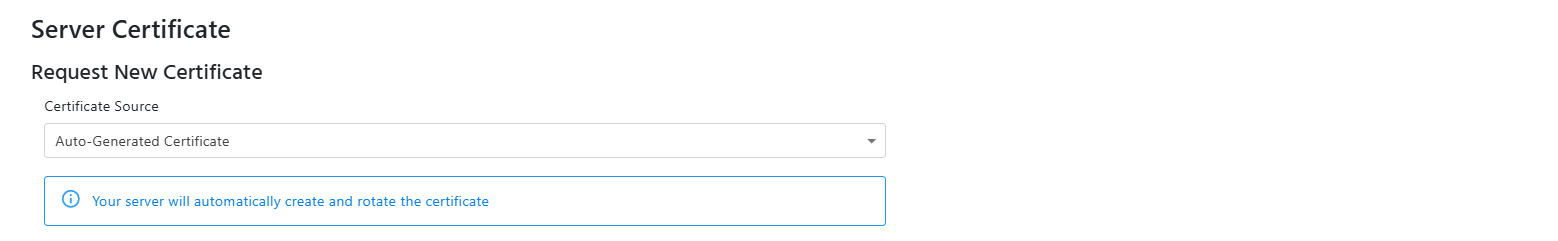
Add Server Certificate to RADIUS Using 3rd Party CA (Option 3)
- If you are using a 3rd party CA, ensure that “Local CA” is set as the certificate source.
- Click the Create CSR button.
- Download the CSR by clicking the “Save CSR” button.
- Submit the CSR to your CA and download the certificate and the certificate of your root CA.
- Once you have the certificate, scroll down and either copy and paste the certificate PEM content or click on “Upload Certificate” and select the certificate in PEM format.
- After you upload your certificate, you must upload the certificate of the Root CA that signed the certificate. Scroll down and either copy and paste the certificate PEM content or click on “Upload Root CA Certificate” and select the certificate in PEM format.
- Now that you have added both the server certificate and the root CA certificate, we can move on to creating the access policies. (Please note that this has not been saved yet, we must add the access policies and click save to save the policy.)
Add Access Policies to RADIUS Network Policy
Up until now we can say that we have setup the equivalent of the RADIUS server (what networking devices to trust, the CAs, and the server certificate) now we can add the access policies. Access policies define the conditions under which a user or device can connect to your network. Each policy can have multiple access policies and they are checked in the order they are sorted.
- You will see an empty new access policy, under the red “No Access Policies” text.
- Enter the name of the access policy. This is just for your records. In this example I will set our RADIUS server as if it was for a school, so I will name the access policy “Students”.
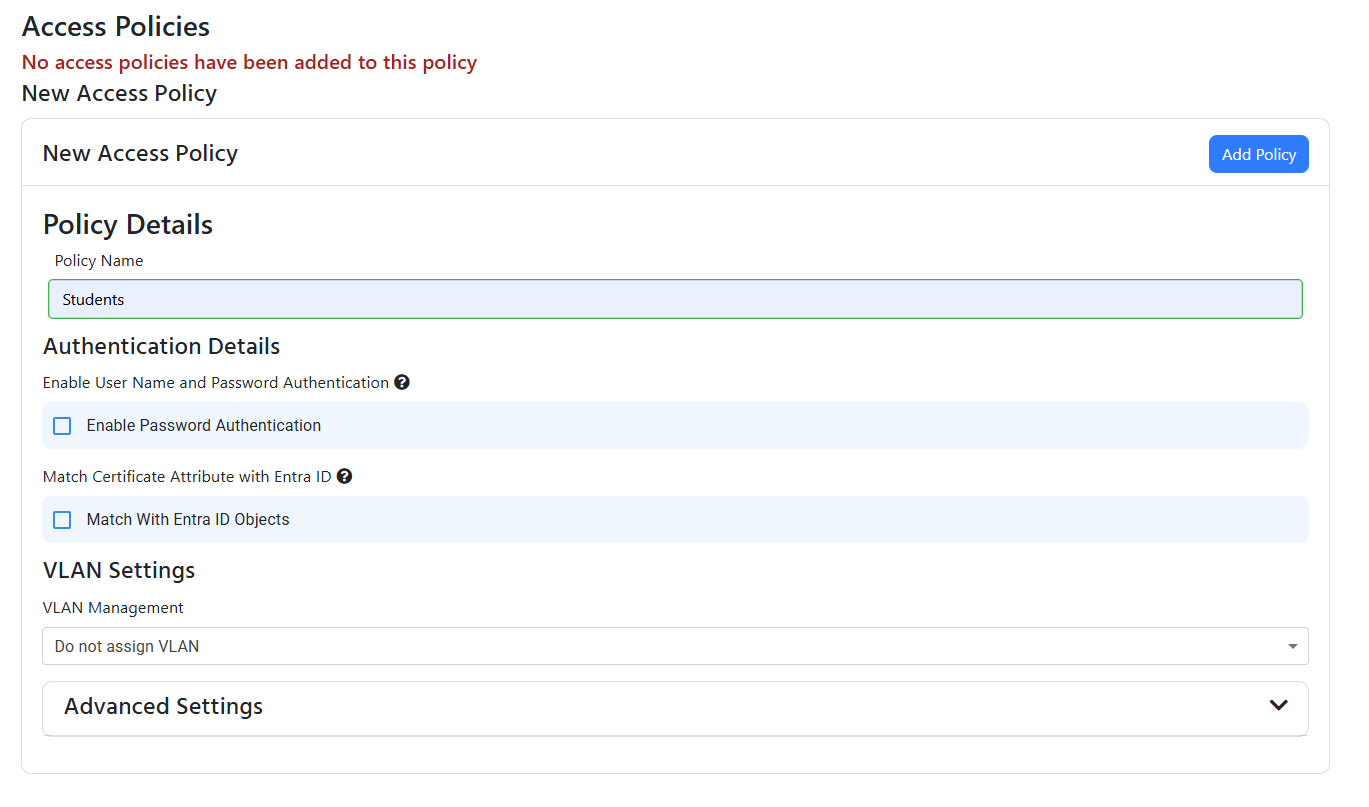
- For this policy we only want to enable EAP-TLS, so we will leave the “Enable Password Authentication” checkbox unchecked.
- EZRADIUS check CRLs (Certificate Revocations Lists) by default, if in addition to CRLs you want to check OCSP, you can check the “Enable OCSP” checkbox. you can read more about the difference between CRL and OCSP here
- Now we must select how we are going to validate that the certificate is from a student the options are:
- CA Matching: If you only issue certificates for students from these CAs, then you can leave everything unchecked. and just assign the VLAN if required.
- Entra ID User Matching: EZRADIUS can extract the user UPN or user ID from a field of the certificate and validate with Entra ID that the user exists and even assign VLAN based on the groups the user is a member of.
- Entra ID Device Matching: EZRADIUS can extract the Entra ID device ID from a field of the certificate and validate with Entra ID that the device exists and even assign VLAN based on the groups the device is a member of.
- Intune Device Matching: EZRADIUS can extract the Intune device ID from a field of the certificate and validate with Intune that the device exists and is compliant with your Intune policies.
- Below we will explain how to set up each of the matching options. Once you are adding your policies, scroll up to the top and click “Save Changes” to save the policy.
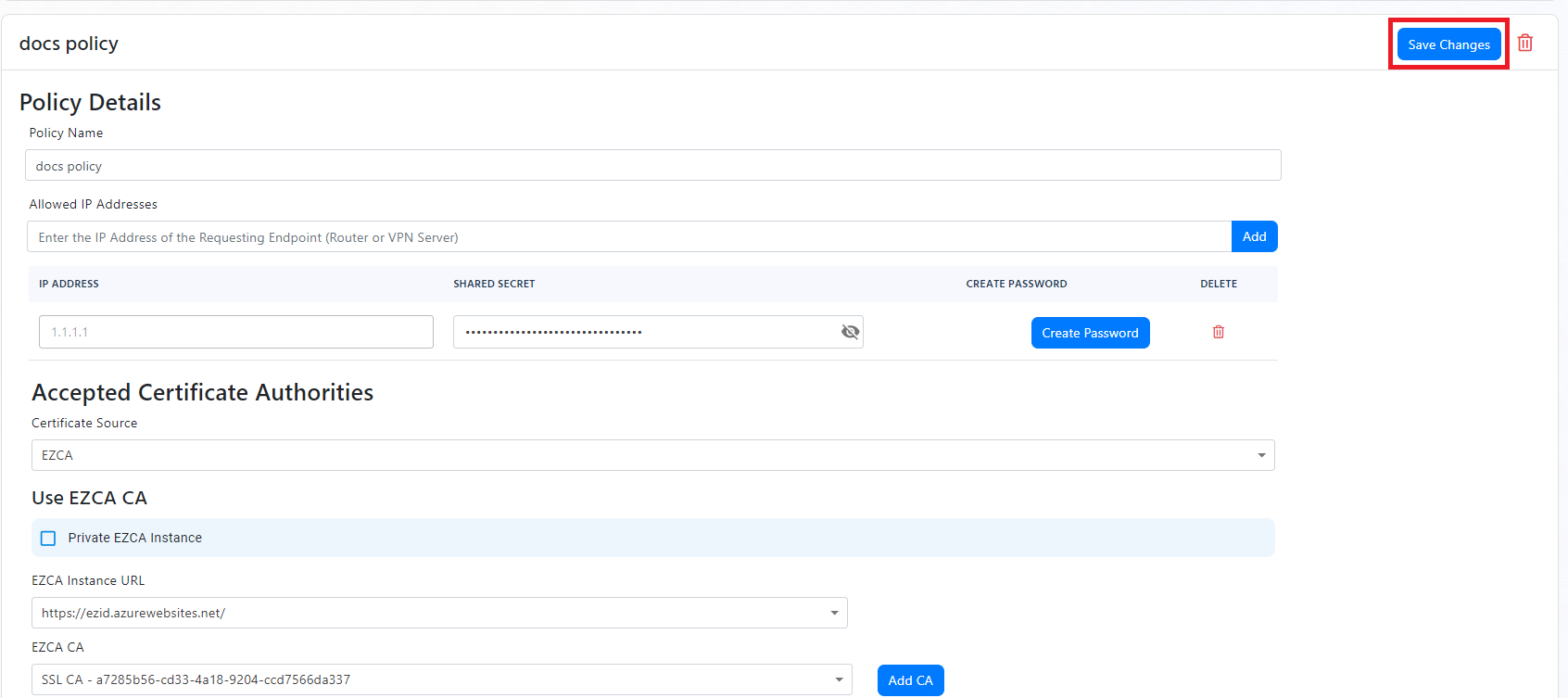
CA Matching
- If you want to only use CA matching and allow any certificate from the CAs you have added to the policy, you can leave the “Match With Entra ID Objects” checkbox unchecked.
- If you want to assign a VLAN to this policy, jump to the VLAN assignment section of this document. Else click “Add Policy” to add the policy to the list of access policies.
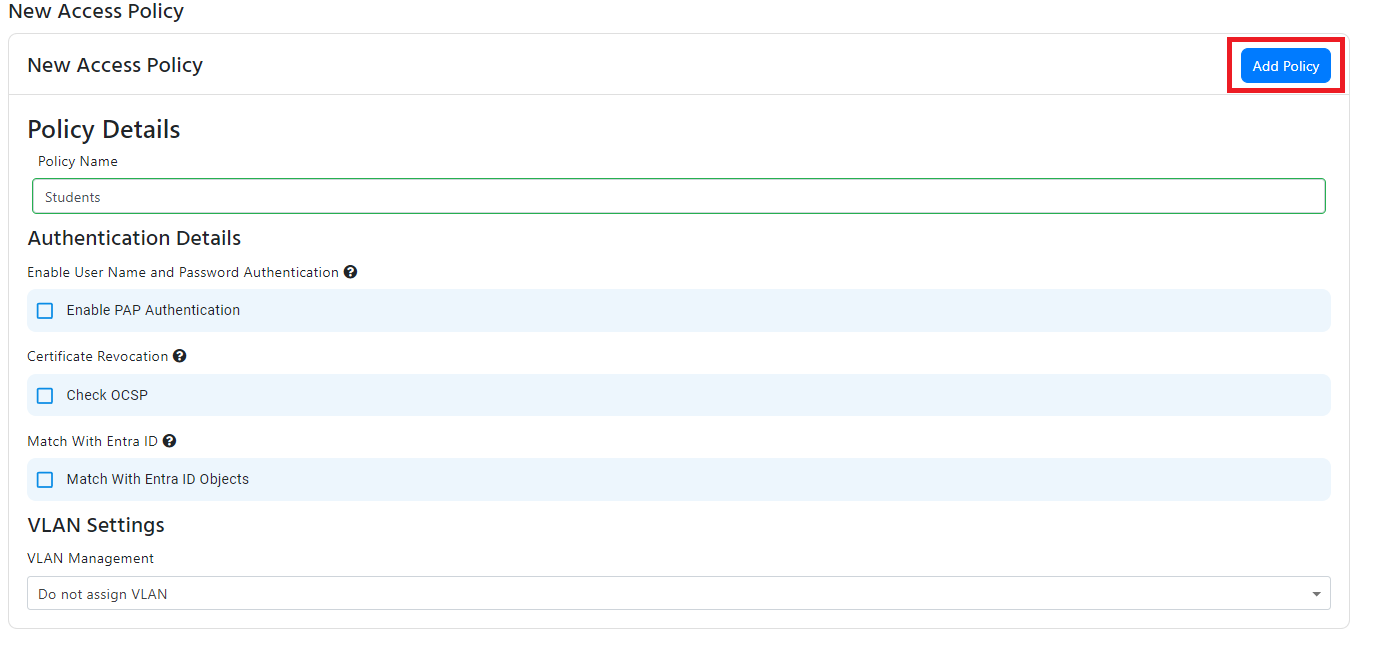
Entra ID User Matching
- If you want to match the user UPN or user ID from the certificate with an Entra ID user, check the “Match With Entra ID Objects” checkbox.
- Select “User” from the in the Certificate Type radio buttons.
- Select the field in the certificate that contains the user UPN or user ID.
- This will now validate that the user exists in Entra ID, if you want to also check if the user is a member of a group, check the “Check Group Membership” checkbox and enter the group name.
- If you want to assign a VLAN to this policy, jump to the VLAN assignment section of this document. Else click “Add Policy” to add the policy to the list of access policies.
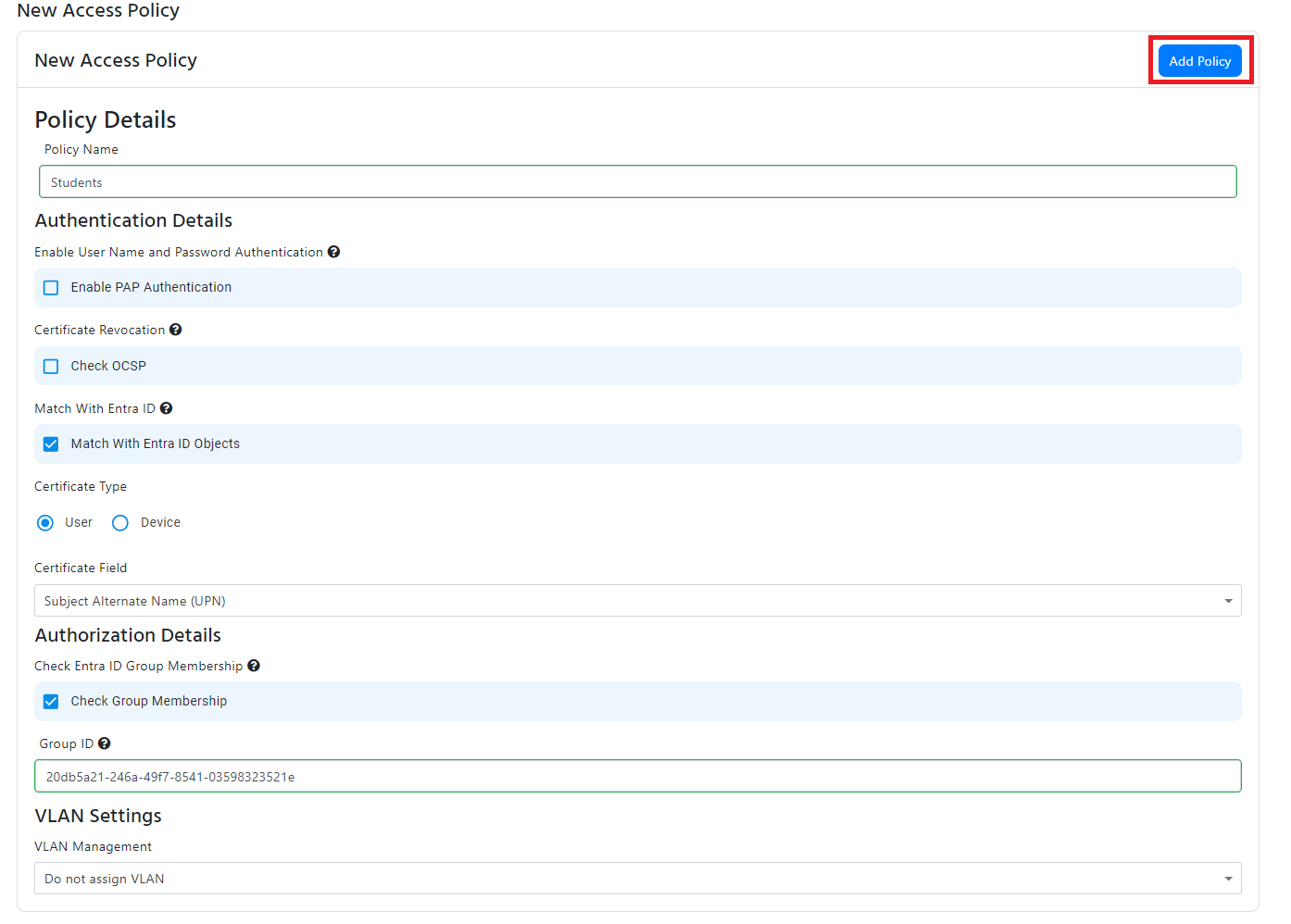
Entra ID Device Matching
- If you want to match the device ID from the certificate with an Entra ID device, check the “Match With Entra ID Objects” checkbox.
- Select “Device” from the in the Certificate Type radio buttons.
- Select “AAD Device ID” from the in the Device Identifier dropdown.
- Select the certificate field in the certificate that contains the device ID.
- If you are using a Subject alternative name, it will also give you de ability to remove the prefix from the device ID (for example if your certificate has deviceid:// you enter deviceid:// as the prefix and EZRADIUS knows to ignore that when validating your certificates).
- This will now validate that the device exists in Entra ID, if you want to also check if the device is a member of a group, check the “Check Group Membership” checkbox and enter the group name. Note that the device must be a member of the group in Entra ID, nested groups are not supported
- If you want to assign a VLAN to this policy, jump to the VLAN assignment section of this document. Else click “Add Policy” to add the policy to the list of access policies.
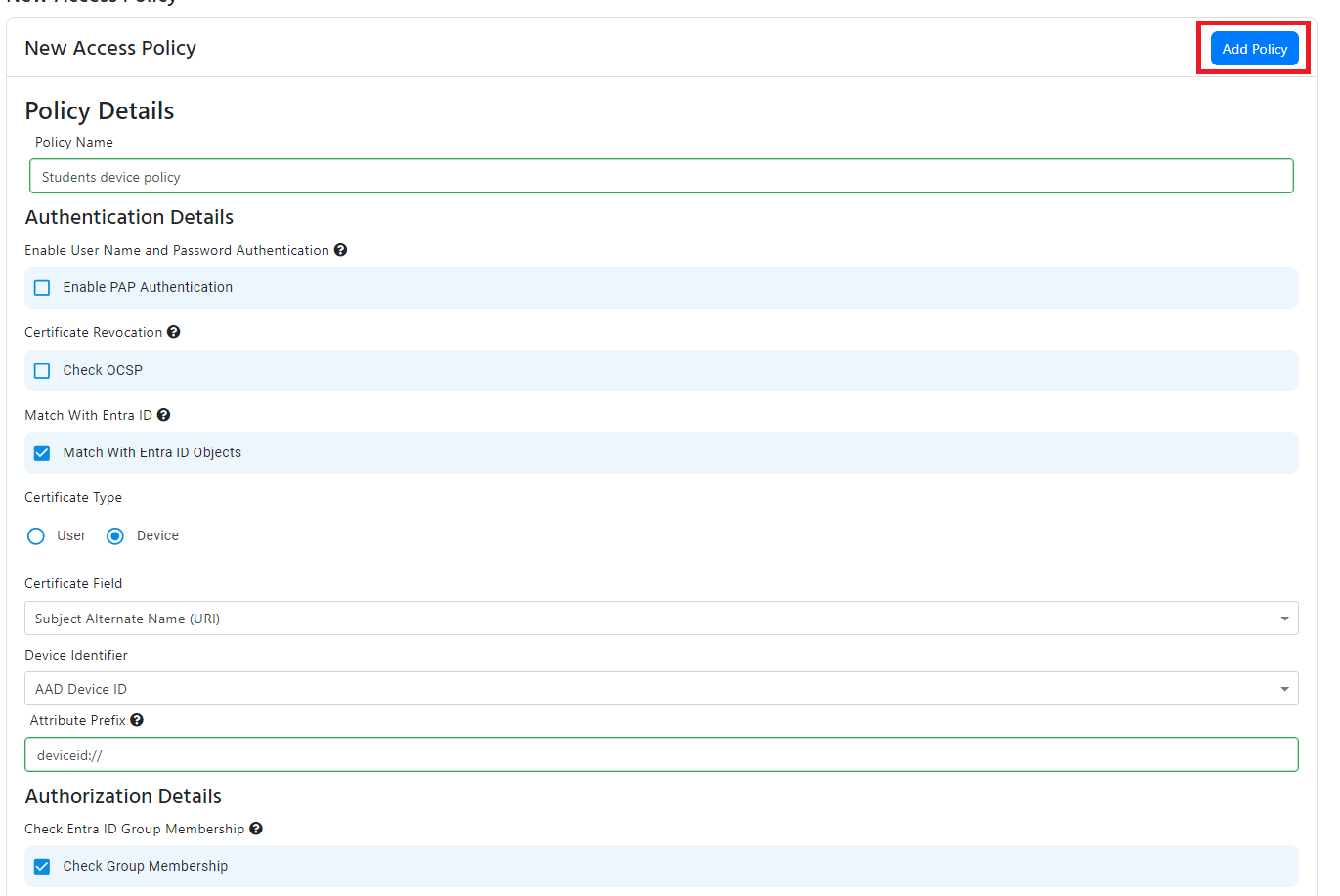
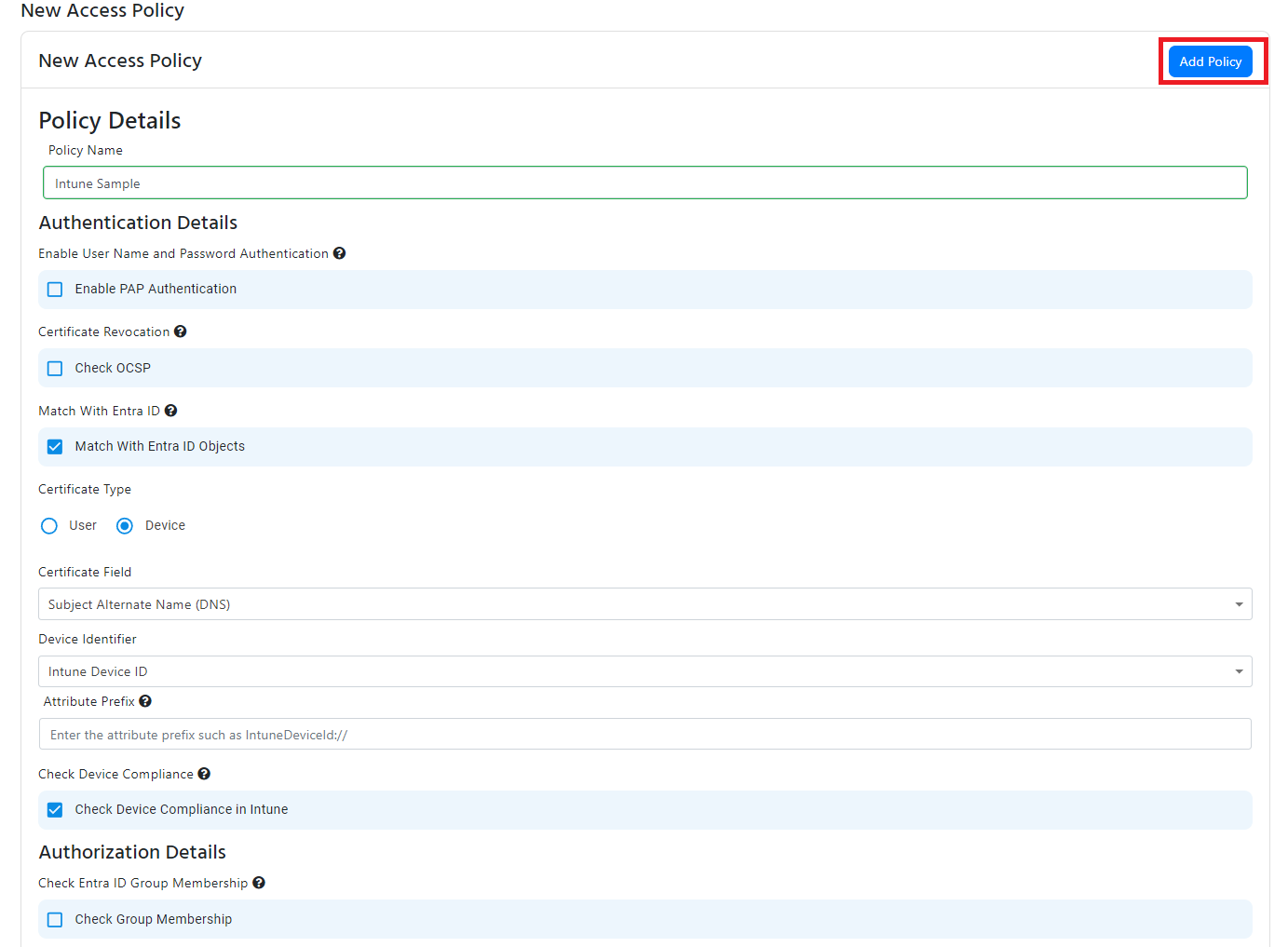
Intune Device Matching
- If you want to match the Intune Device ID from the certificate with an Intune device, check the “Match With Entra ID Objects” checkbox.
- Select “Device” from the in the Certificate Type radio buttons.
- Select “Intune Device ID” from the in the Device Identifier dropdown.
- Select certificate the field in the certificate that contains the Intune device ID.
- If you are using a Subject alternative name, it will also give you de ability to remove the prefix from the device ID (for example if your certificate has IntuneDeviceId:// you enter IntuneDeviceId:// as the prefix and EZRADIUS knows to ignore that when validating your certificates).
- This will now validate that the device exists in Intune, if you want to also check if the device is compliant with your Intune policies, check the “Check Device Compliance in Intune” checkbox.
- If you also want to check if the device is a member of a group, check the"Check Group Membership" checkbox and enter the group name. Note that the device must be a member of the group in Intune, nested groups are not supported
- If you want to assign a VLAN to this policy, jump to the VLAN assignment section of this document. Else click “Add Policy” to add the policy to the list of access policies.
VLAN Assignment
The default setting will not set a VLAN, however, if you want to assign a VLAN based on the access policy, you can do so in two ways:
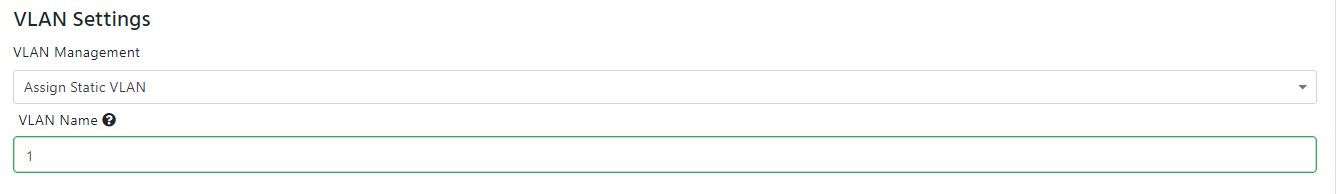
- Static VLAN Assignment: If you want to assign a static VLAN to the policy, you can select “Assign Static VLAN” from the drop down and you can enter the VLAN ID in the VLAN Name field.
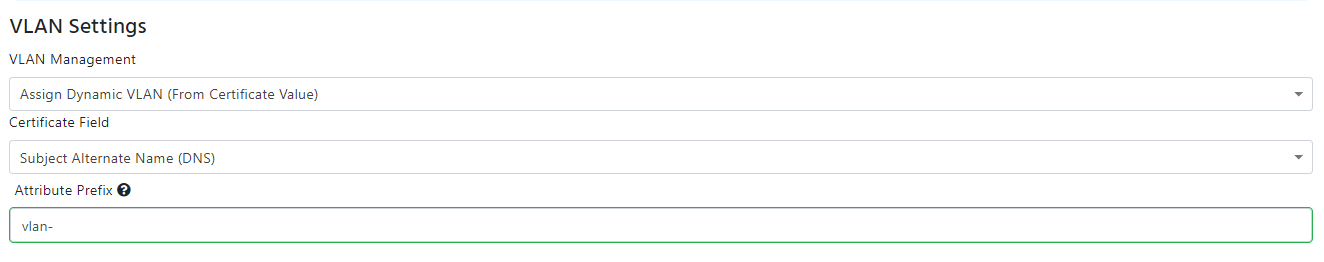
- Dynamic VLAN Assignment Based on Certificate Value: If you want to assign a VLAN based on a value in the certificate, you can do so by selecting the “Assign Dynamic VLAN (From Certificate Value)” from the VLAN management dropdown selecting the field in the certificate that contains the VLAN ID. Same as with the device ID, if you are using a Subject alternative name, it will also give you de ability to remove the prefix from the VLAN ID (for example if your certificate has vlan:// you enter vlan:// as the prefix and EZRADIUS knows to ignore that when assigning your VLANs).
- Once you have added the access policies and the VLAN assignment, scroll up to the top and click “Save Changes” to save the policy.
Advanced Settings
While most of the settings are already set up for you, there are some advanced settings that you can configure to further customize your network policies. These settings are optional and can be used to further refine the access policies.
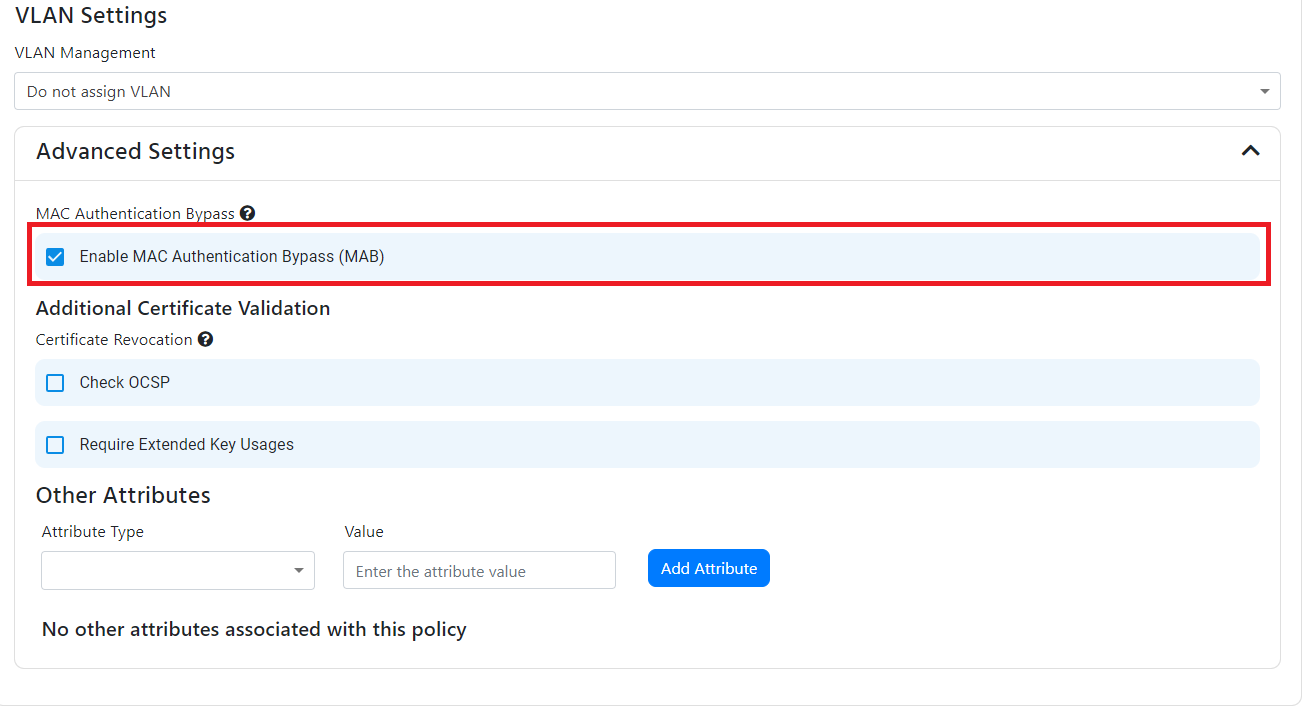
How To Enable MAC Authentication Bypass
If you want to enable MAC Authentication Bypass, you can do so by checking the “Enable MAC Authentication Bypass” checkbox. This will allow devices to connect to the network without a certificate if they have a MAC address that is in the MAC address list. You can add MAC addresses to the list following this guide
How To Enable OCSP Checking
EZRADIUS check CRLs (Certificate Revocations Lists) by default, if in addition to CRLs you want to check OCSP, you can check the “Enable OCSP” checkbox. you can read more about the difference between CRL and OCSP here
Matching Attributes in Request Such as SSID
By adding attributes to this setting, the access policy will only be passed if the router or access point sends the denoted attributes to the EZRADIUS server. Below are the descriptions and use cases for matching the supported attributes:
- Calling-Station-ID: Usually set-up to contain the SSID of the network or the MAC address of a device when carrying out MAC-Authentication-Bypass
- NAS Identifier (NAS-ID): Usually set-up to contain the SSID of the network or the MAC address of a device when carrying out MAC-Authentication-Bypass
Send Attributes in Accept
By adding attributes to this setting, an authentication request that matches with the following access policy will send the denoted attributes in the Access-Accept response sent to the router or access point. The Access-Accept response is sent when the identity in the authentication request is authorized. Below are the descriptions and use cases for the supported attributes that can be sent on success:
- Filter-Id: Can be used to assign a pre-defined access control list (ACL) to the user that successfully authenticates with the access policy
- Cisco-AVPair: Cisco-specific attribute
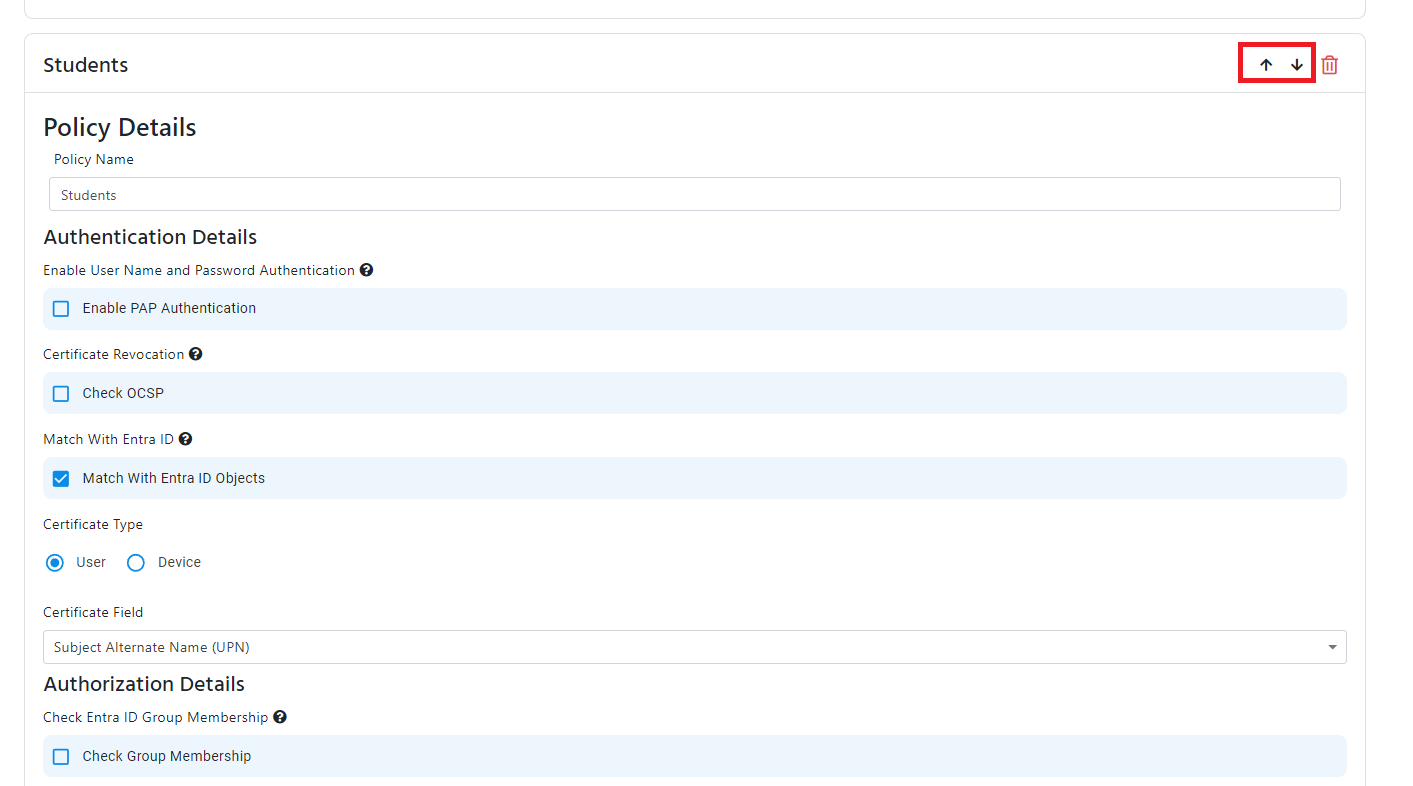
Access Policy Order
The access policies are checked in the order they are sorted, you can change the order of the access policies by clicking on the up and down arrows on the right side of the access policy.
- Once your policy is ready, click “Save Changes” at the top to save the policy changes.