How To Set Up 802.1X Network Authentication on Ubuntu
Note: While this guide is written for Ubuntu, these set of instructions should be the same with any other Linux distribution that runs GNOME with NetworkManager.
Note: While you can manually configure your Ubuntu device to connect to an enterprise 802.1X network, we highly recommend using a Mobile Device Management (MDM) solution like Microsoft Intune to push the necessary network profiles and certificates to your devices. This ensures that all devices are consistently configured and reduces the risk of misconfiguration.
What is 802.1X Network Authentication?
At home, you probably just plug your computer into an ethernet cable or connect to a Wi-Fi network using a single password. It’s easy and convenient because at home you (usually) trust everyone who can connect to your network. However, in an enterprise environment, you want to make sure that only authorized users and devices can connect to your network. This is where 802.1X network authentication comes in. 802.1X is a network protocol that provides an authentication mechanism to devices wishing to attach to a LAN or WLAN. It is commonly used in enterprise networks to provide secure access to network resources.
Enterprise networks require a higher level of security and configuration than home networks. Instead of a single password, enterprise networks use RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) servers to authenticate users and devices. To establish a secure connection, devices need to have the correct network profiles and certificates installed. These tell the device what security protocols to use (EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, etc.) and which RADIUS servers to trust. Without these profiles and certificates, your device won’t know how to connect securely to the network. That’s why devices will fail to connect to enterprise networks if they are not properly configured.
How to Download and Prepare the User Certificate and CA Certificate for EAP-TLS on Ubuntu
To connect to a Wi-Fi network using EAP-TLS certificate-based authentication, you need to have a client certificate and private key in PEM format. Follow these steps to prepare your certificates:
How to Create a New User Certificate for EAP-TLS
Begin by downloading or creating a user certificate for EAP-TLS authentication. Depending on your setup, you can use one of the following methods:
Refer to this guide for instructions on how to create and download a user certificate for EAP-TLS authentication using the EZCA Self-Service Portal. Make sure to download the certificate in PEM format along with the private key.
Refer to this guide for instructions on how to automatically install a SCEP certificate for EAP-TLS authentication using a script on Linux.
If you are using a 3rd party PKI, refer to your PKI documentation to create and download a user certificate for EAP-TLS authentication. Make sure to download the certificate in PEM format along with the private key.
You should now have a PEM formatted client certificate and CA certificate on your local machine:
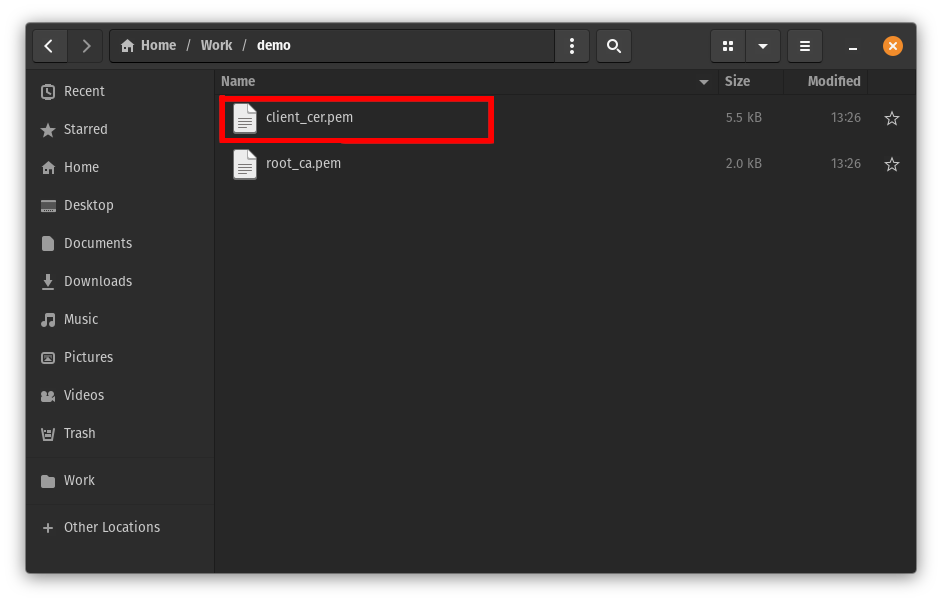
How to Prepare the User Certificate and Private Key
If the private key is unencrypted, encrypt the private key with OpenSSL using the following command. Make sure that the private key and the certificate file are separate. This is a limitation with NetworkManager.
openssl rsa -aes256 -in $FILE_WITH_PRIVATE_KEY -out $FILE_NAME_FOR_ENCRYPTED_PRIVATE_KEY
How to Trust Your RADIUS Server CA Certificate on Ubuntu
For your Ubuntu device to trust the RADIUS server during the authentication process, you need to install the RADIUS server CA certificate on your device. This tells your Ubuntu device to trust all RADIUS servers that present a certificate signed by this CA during the authentication process.
How to Download Your Radius Server CA Certificate
If you used the EZRADIUS auto-generated certificate for your RADIUS server, you’ll just have a single CA certificate to download. Follow these steps:
-
Log in to your EZRADIUS portal.
-
Navigate to Policies.
-
Select the policy you are using for Entra ID Password Authentication.
-
Scroll down to the Server Certificate section.
-
Click on the Download CA Certificate button to download the certificate to your local machine. It will have a filename similar to
RootCA.cer.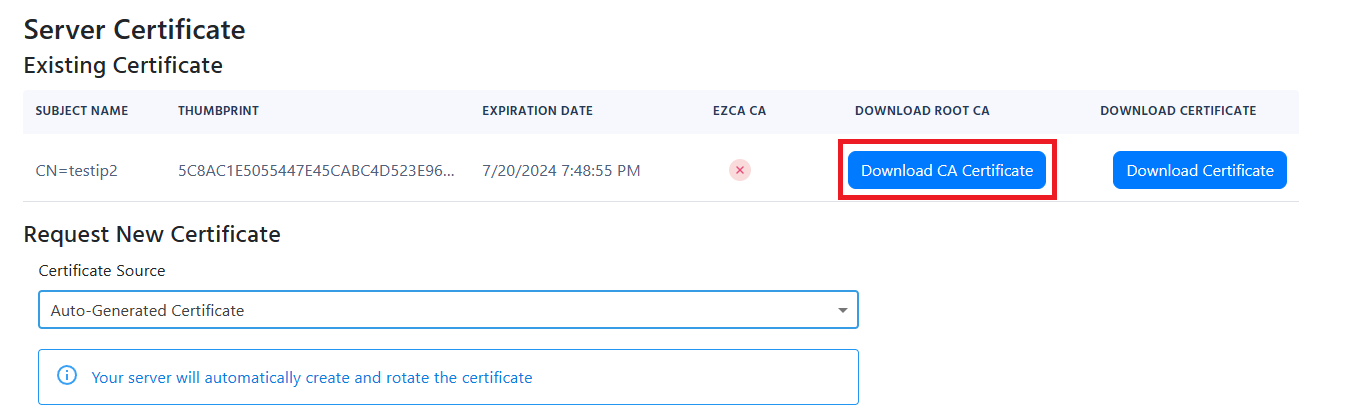
If you used the EZRADIUS EZCA to issue your RADIUS server certificate, you’ll need to download the the CA certificate for your EZCA CA, plus the Root CA certificate, if applicable. Follow these steps:
-
Log in to your EZCA portal.
-
Navigate to Certificate Authorities.
-
Select the CA that issued your RADIUS server certificate.
-
Click on the View Details button.
-
Click on the Download Certificate button to download the CA certificate to your local machine. It will have a filename similar to
<CA-NAME>.cer. -
If your EZCA CA is an intermediate CA, make sure to also download the Root CA certificate by repeating the above steps for the Root CA.
Refer to your PKI documentation to download the CA certificate(s) that issued your RADIUS server certificate. Ensure you have the root CA and any intermediate CA certificates if applicable.
How to Install the RADIUS Server CA Certificate on Ubuntu
To install the RADIUS server CA certificate on your Ubuntu device, follow these steps:
- Open the Files application and navigate to the location where you downloaded the RADIUS server CA certificate (e.g.,
RootCA.cer). - Right-click on the certificate file and select Open With Other Application.
- Choose Certificates from the list of applications and click Select.
- In the Certificates application, click on the Install Certificate button.
- Select System as the location to install the certificate and click Continue.
- You may be prompted to enter your Ubuntu administrator password to authorize the installation. Enter your password and click Authenticate.
- After the installation is complete, close the Certificates application.
How to Set Up Your Network for RADIUS Authentication on Ubuntu
When connecting your Ubuntu device to an enterprise network using RADIUS authentication, you need to ensure that the correct EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) method is configured based on your authentication setup.
How To Connect to an EAP-TLS Wi-Fi Network on Linux
-
Open the Settings application on your Ubuntu device.
-
Navigate to the Wi-Fi section and select the desired Wi-Fi network
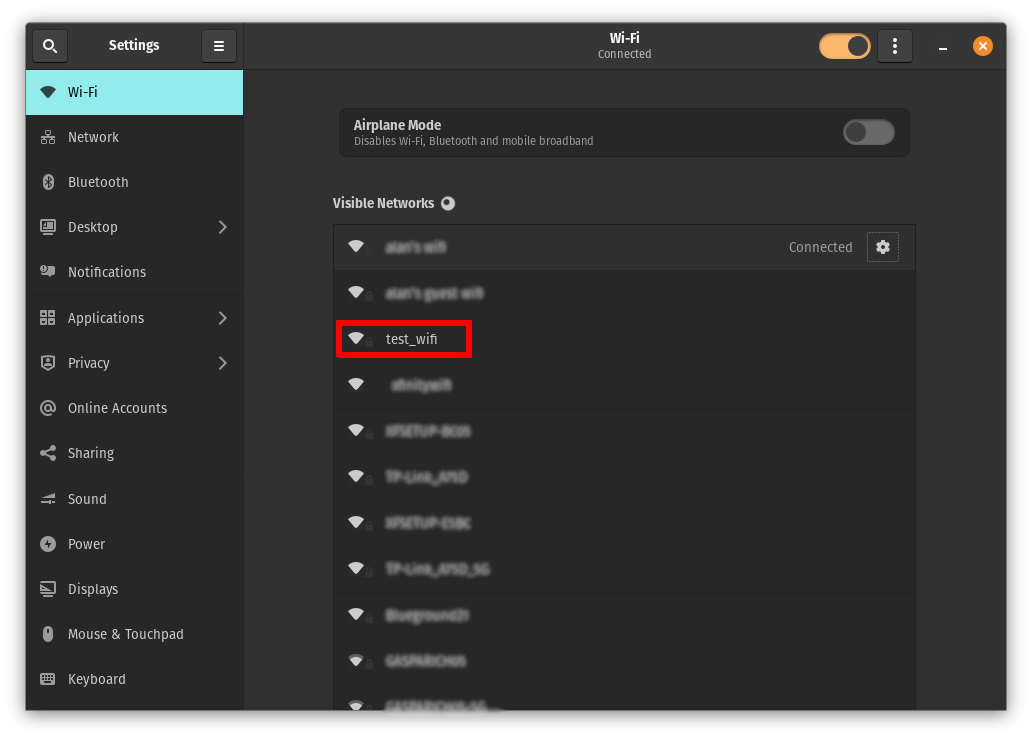
-
Make sure Security is set to WPA & WPA2 Enterprise (or WPA3-Enterprise if your network uses WPA3)
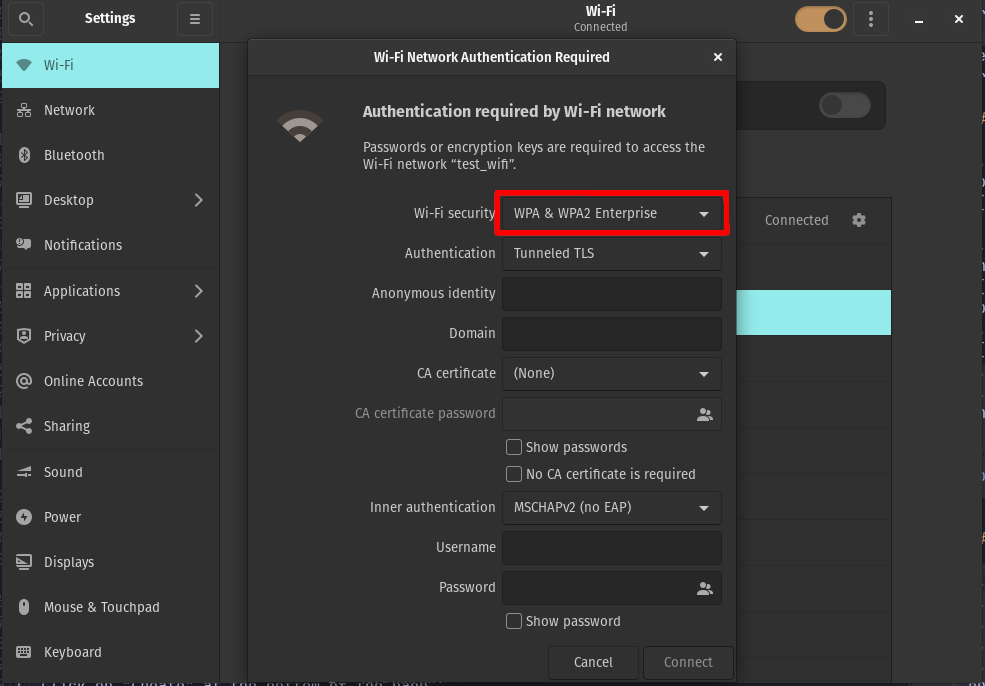
-
Change Authentication to TLS.
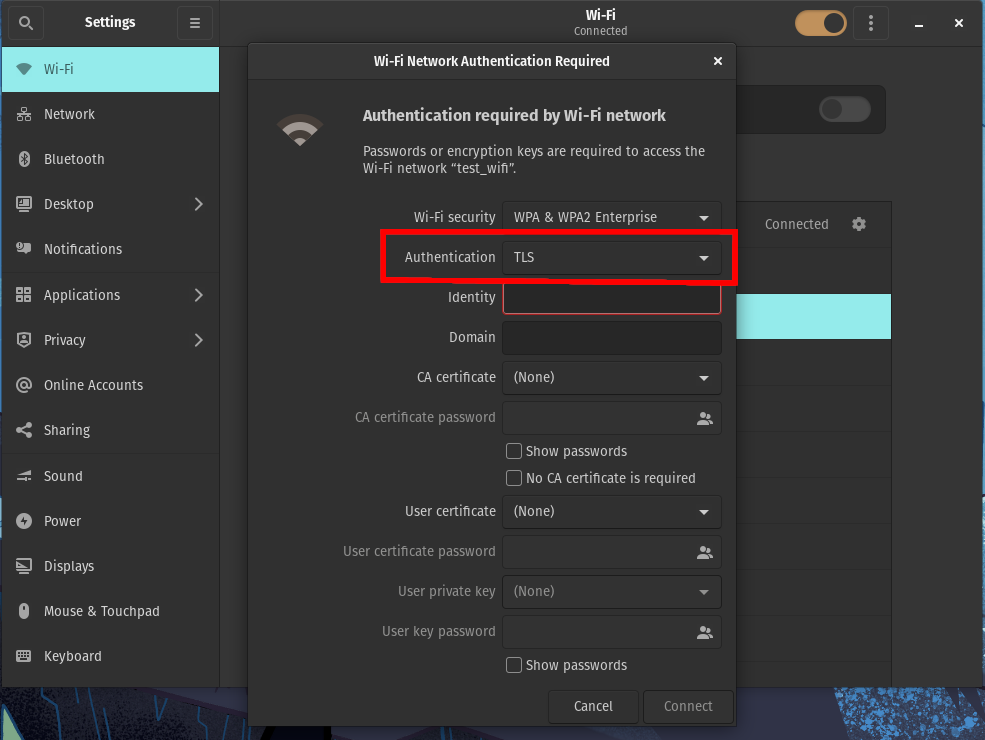
-
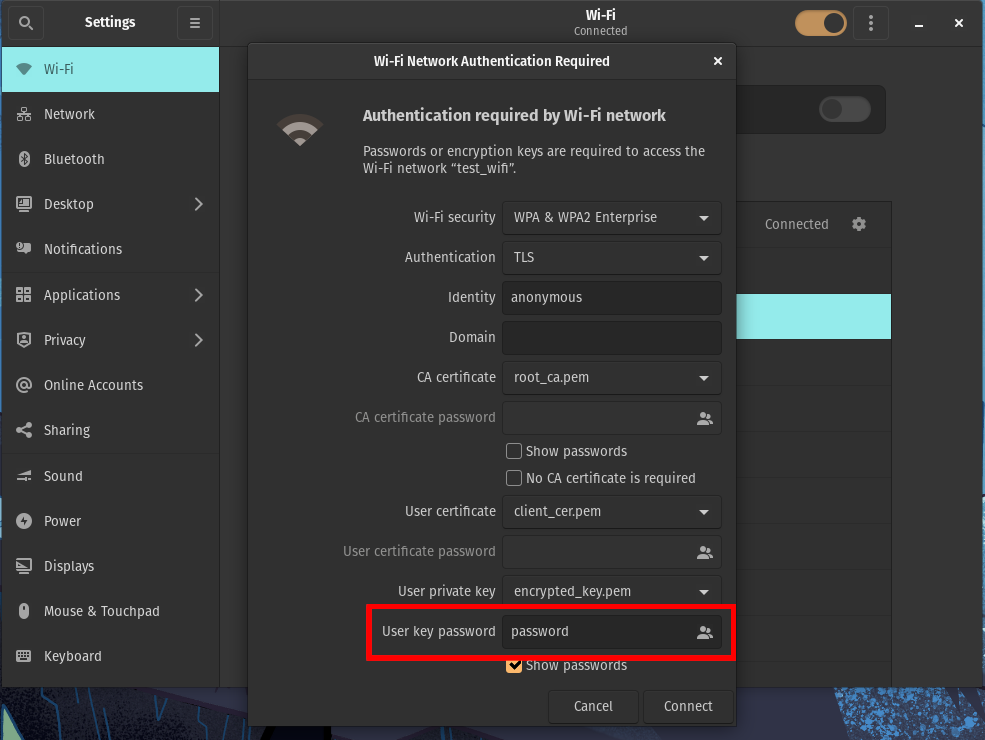
Set Identity to
anonymous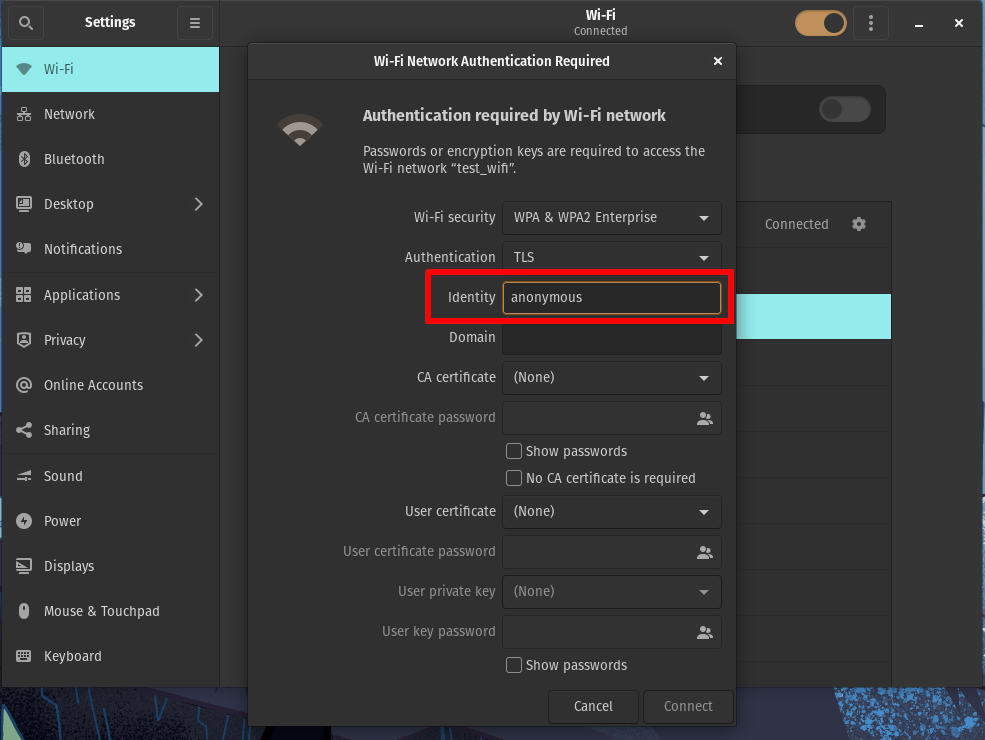
-
For CA certificate, select the CA root certificate you downloaded earlier (not to be confused with the RADIUS server certificate).
-
For User certificate, select your client certificate file in PEM format.
-
For Private key, select your encrypted private key file in PEM format.
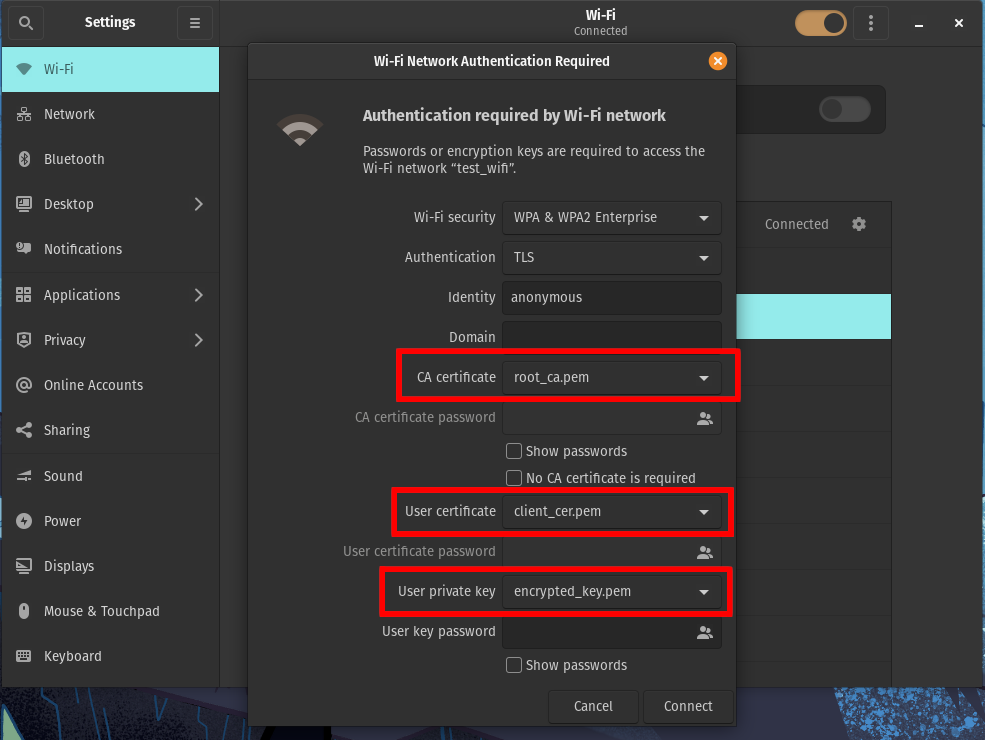
-
Enter the User key password you used to encrypt the private key earlier.
-
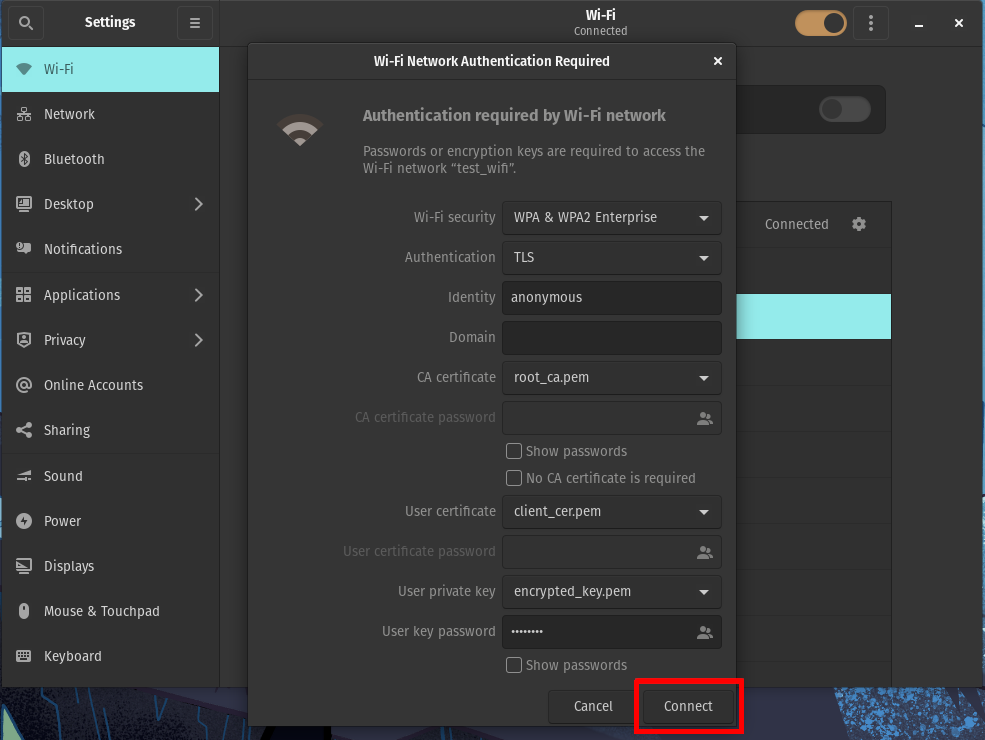
Click Connect to connect to the network.
-
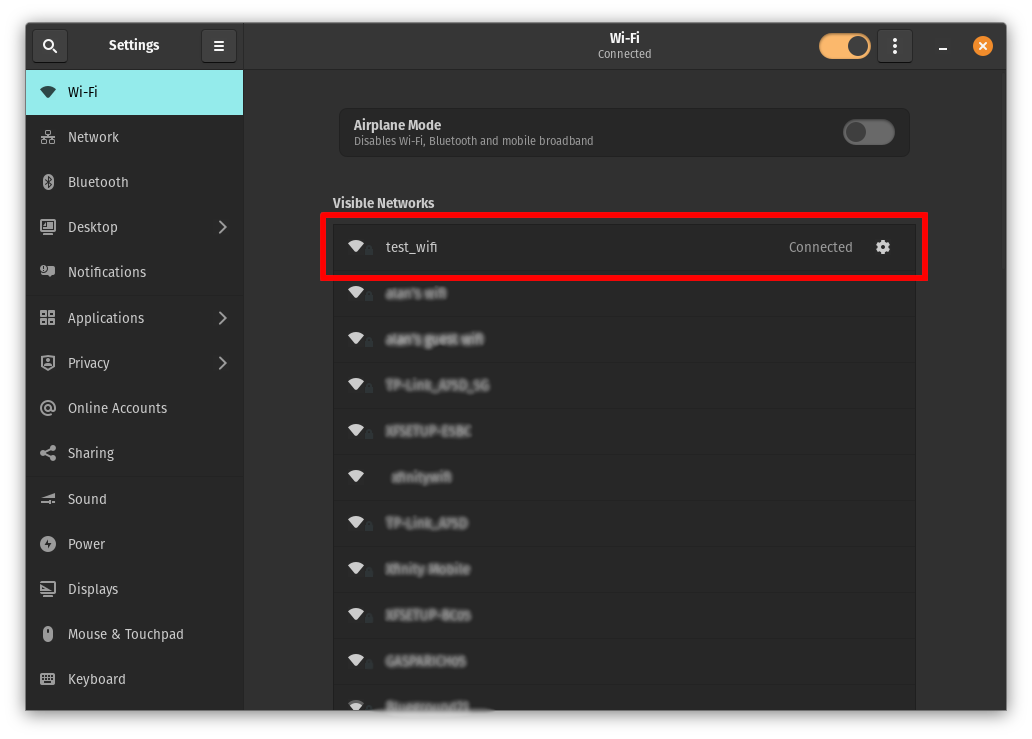
You should now be connected to the network with certificate authentication using EAP-TLS
How to Set Up EAP-TLS Certificate Based Authentication with SCEP Certificate for Wi-Fi on Ubuntu
- Make sure the SCEP Certificate Authority which issued your SCEP certificate is trusted by your EZRADIUS policy
- Copy the following script to a file, fill the values as required, and run it
- If you are using an auto-generate server certificate, leave both
CA_PATHandEZCA_SERVER_CA_STATIC_SCEP_URLempty. Set theEZCA_SERVER_CA_STATIC_SCEP_URLif the server certificate CA is a SCEP EZCA certificate, else, manually download the CA certificate and put the absolute path to the CA file inCA_PATH - Set the SSID of the wifi network in
SSID
- If you are using an auto-generate server certificate, leave both
#!/bin/bash
# User-set values
# CA_PATH= # Set to the absolute path of the server certificate CA
# EZCA_SERVER_CA_STATIC_SCEP_URL=
# SSID= # SSID of the wireless network
# NOTE: if the server certificate is set to be auto-generated, leave the CA_PATH empty and
# the script will install the autogenerated CA. If you are using a server certificate
# generated from EZCA, the script will also install it automatically if you put down your
# EZCA server certificate CA static scep URL
## ---------- ## ---------- ## ---------- ## ---------- ## ---------- ##
# Check all required executables exist
req_execs=("base64" "cat" "curl" "cut" "grep" "head" "mkdir" "nmcli" "sed")
for exe in "${req_execs[@]}"; do
if [ ! $(command -v "$exe") ]; then
echo "Required executable $exe not found"
exit 1
fi
done
SSID=${SSID:-'DEFAULT_SSID'}
CONNECTION_NAME=${CONNECTION_NAME:-'keytos-ezradius-eap-tls'}
SCEP_CER_DIR=${SCEP_CER_DIR:-"$HOME/.local/share/keytos/scep_certs"}
KEY_PWD_PATH=$SCEP_CER_DIR/key.pwd
ENCRYPTED_KEY_PATH=$SCEP_CER_DIR/key.encrypted.pem
CER_PATH=$SCEP_CER_DIR/certificate.pem
WIFI_NIC=$(nmcli -t -f DEVICE,TYPE device | grep wifi$ | head -n 1 | cut -d: -f1)
if [ -z "$WIFI_NIC" ]; then
exit 1
fi
nmcli -f GENERAL.STATE con show "$CONNECTION_NAME" > /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
exit 0
fi
# Get CA for the auto-generated certificate, if server certificate is custom it must
# be manually installed and passed above
if [ ! -f $CA_PATH ]; then
INSTALL_DIR=${INSTALL_DIR:-"$HOME/.local/share/keytos/ezradius"}
mkdir -p $INSTALL_DIR
CA_PATH=$INSTALL_DIR/server_ca_certificate.pem
EZCA_SERVER_CA_STATIC_SCEP_URL=${EZCA_SERVER_CA_STATIC_SCEP_URL:-'https://portal.ezca.io/api/SCE
curl ${EZCA_SERVER_CA_STATIC_SCEP_URL}?operation=GetCACert \
| base64 \
| sed '1i -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----' \
| sed '$a -----END CERTIFICATE-----' \
> $CA_PATH
fi
# Check files exist
if [ ! -f $CA_PATH ] || [ ! -f $CER_PATH ] || [ ! -f $ENCRYPTED_KEY_PATH ] || [ ! -f $KEY_PWD_PATH ]; then
exit 1
fi
nmcli c add type wifi ifname "$WIFI_NIC" con-name "$CONNECTION_NAME" \
802-11-wireless.ssid "$SSID" \
802-11-wireless-security.key-mgmt wpa-eap \
802-1x.eap tls \
802-1x.identity 'anonymous' \
802-1x.ca-cert "$CA_PATH" \
802-1x.client-cert "$CER_PATH" \
802-1x.private-key "$ENCRYPTED_KEY_PATH" \
802-1x.private-key-password "$(cat $KEY_PWD_PATH)"
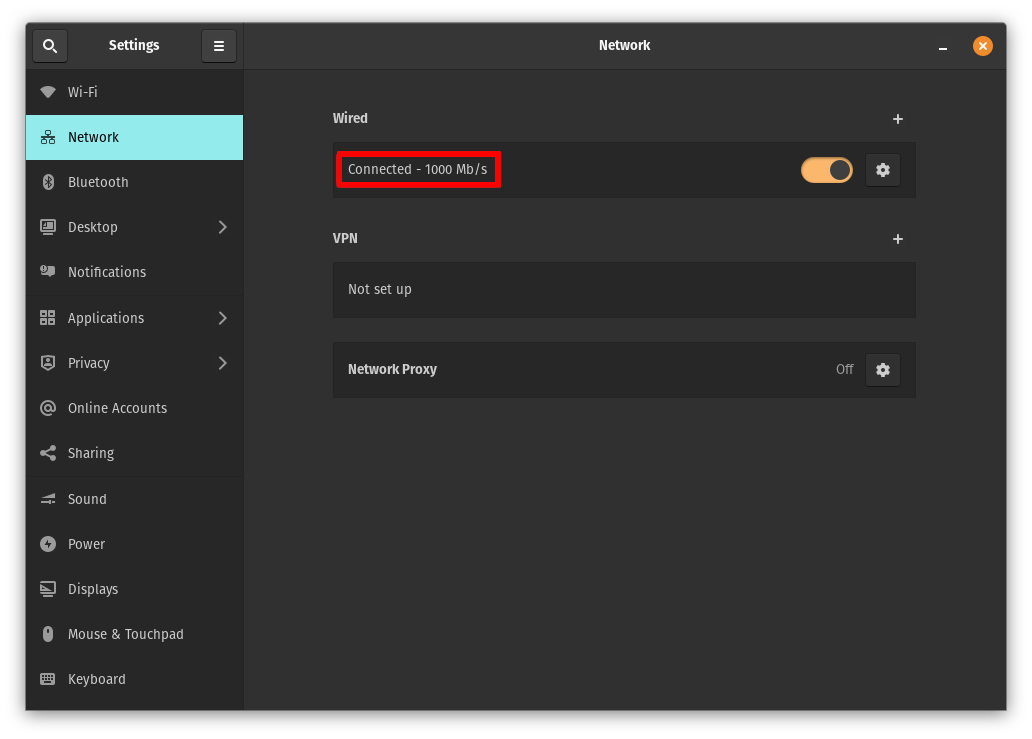
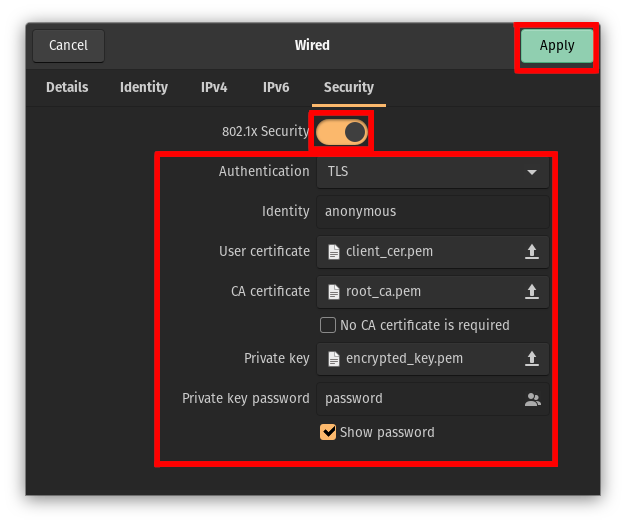
How To Connect to an EAP-TLS Wired Network on Linux
-
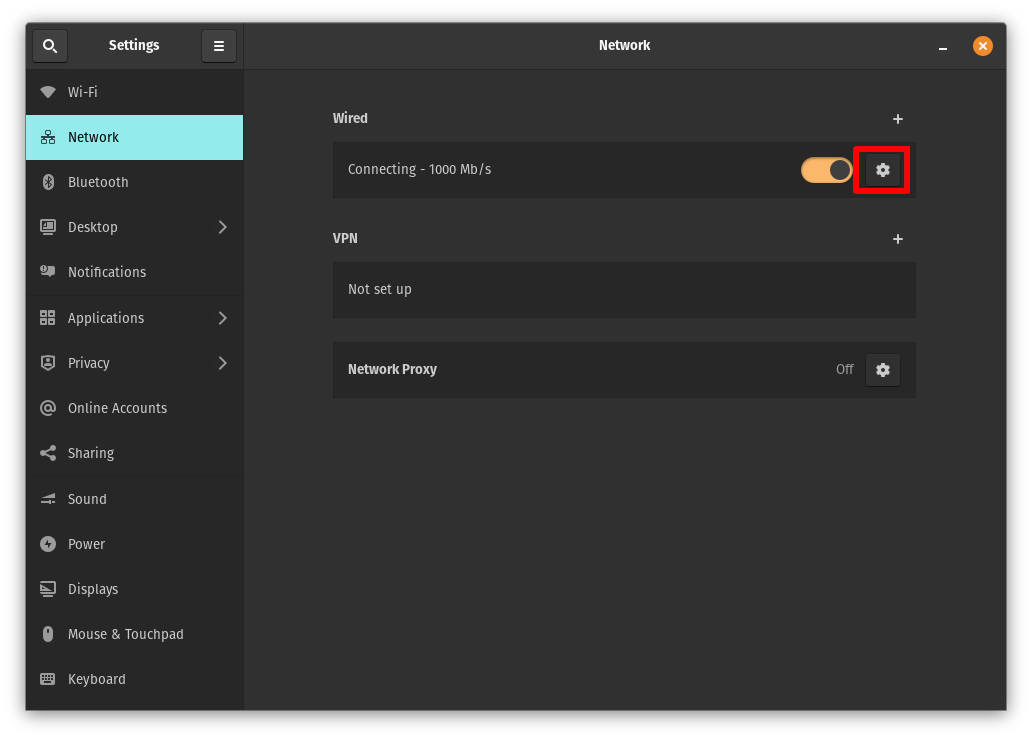
Open Settings and go to the Network tab. Click the gear icon next to the Wired connection to open the settings.
-
Under Security enable 802.1x Security.
-
Set Authentication to TLS.
-
Set Identity to
anonymous. -
For the User certificate, select your client certificate file in PEM format.
-
For the CA certificate, select the CA root certificate you downloaded earlier (not to be confused with the RADIUS server certificate).
-
For the Private key, select your encrypted private key file in PEM format.
-
Enter the User key password you used to encrypt the private key earlier.
-
Click Apply to save the settings.
-
You should now be connected to the network.